IGCSE Physics Energy Resources and Energy Transfers Past Papers Exam Questions (Edexcel): 2021-22
We analysed the International GCSE past papers and grouped the questions by topic. Here, you will find questions relating to the topic – Energy resources and energy transfers. Use these to familiarise, practice and prepare for your IGCSE Physics examination.
You can find earlier papers below:
- IGCSE Physics Past Papers Exam Questions on Energy resources and energy transfers 2019-20.
- IGCSE Physics Past Papers Exam Questions on Energy resources and energy transfers 2021-22.
- IGCSE Physics Past Papers Exam Questions on Energy resources and energy transfers 2023-24.
What you need to know
Use the list below as a quick recap for what you need to know before attempting the past year exam questions under this topic. This is based on Edexcel International GCSE in Physics (4PH1) specification with first teaching Sept 2017 and first examination June 2019.
You can find earlier IGCSE Physics Past Year Questions for the Topic Energy resources and energy transfers 2019-20 here.
Paper 1 and 2: (4) Energy resources and energy transfers
Paper 1 covers all the topics except where it is marked “paper 2 only” while Paper 2 covers all topics.
A. UNITS
- kilogram (kg), joule (J), metre (m), metre/second (m/s), metre/second2 (m/s2), newton (N), second (s) and watt (W)
B. ENERGY TRANSFERS
- describe energy transfers from one energy store to another. Energy stores: chemical, kinetic, gravitational, elastic, thermal, magnetic, electrostatic, nuclear. Energy transfers: mechanical, electrical, heating, radiation (light and sound).
- principle of energy conservation.
- relationship between efficiency, useful energy output and total energy input. efficiency=useful energy transferred (output)/total energy supplied (input) ×100%
- describe a variety of everyday and scientific devices and situations for the transfer of the input energyincluding their representation by Sankey diagrams.
- describe how thermal energy transfer may take place by conduction, convection and radiation.
- explain the role of convection in everyday phenomena.
- explain how emission and absorption of radiation are related to surface and temperature.
- investigate thermal energy transfer by conduction, convection and radiation.
- explain ways of reducing unwanted energy transfer such as insulation
C: WORK AND POWER
- relationship between work done, force and distance moved in the direction of force. W=F×d
- work done is equal to energy transferred.
- use the definitions of work and power.
- the relationship for gravitational potential energy, mass, gravitational field strength and height. GPE = m × g × h
- the relationship for kinetic energy. kinetic energy = 1/2 × mass × speed2 (KE = 1/2 ×m×v2)
- how conversation of energy produces a link between gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy and work.
- describe power as rate of transfer of energy or the rate of work
- relationship between power, work done (energy transferred) and time. P = W/t
(paper 2 only)
D. ENERGY RESOURCES AND ELECTRICITY GENERATION
- describe the energy transfers involved in generating electricity (wind, water, geothermal, solar heating, solar cells, fossil fuels, nuclear)
- describe the advantages and disadvantages of large-scale electricity production from various renewable and non-renewable resources.
June 2021 Paper 1P Q10
10 The photograph shows a large hurdle on an athletics track.
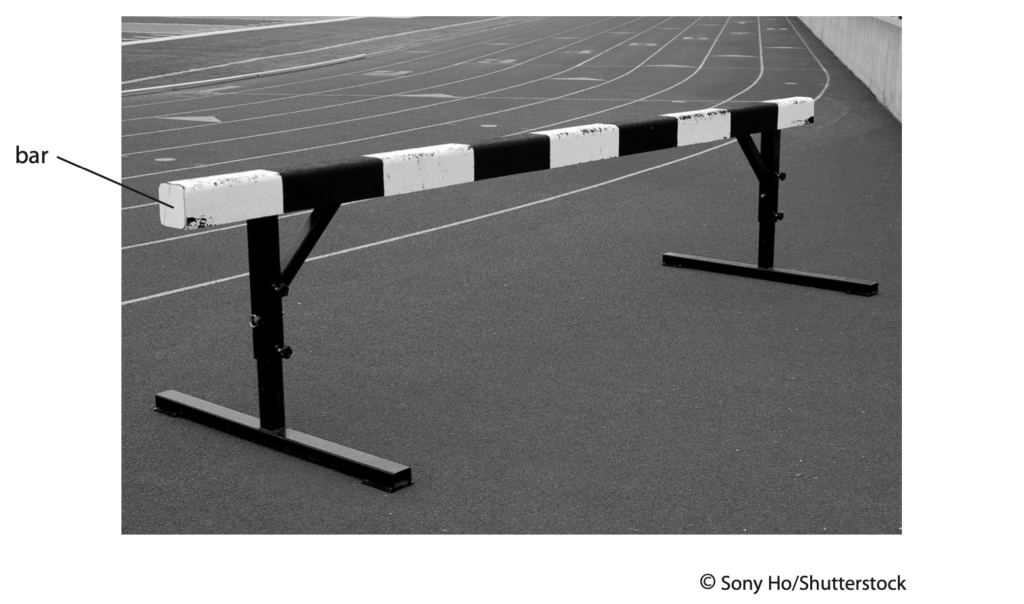

(a) The bar of the hurdle is made of wood and is painted black and white.
The temperature of the hurdle increases when the Sun shines on it.
Explain which part of the bar reaches the highest temperature. (2)
(b) The air near the bar receives energy by heating.
Explain how a convection current is formed in the air near the bar. (4)
(Total for Question 10 = 6 marks)
January 2021 Paper 2P Q4
4 The bar chart gives information about how some of the electrical power in the United States of America (USA) was generated in the year 2018.
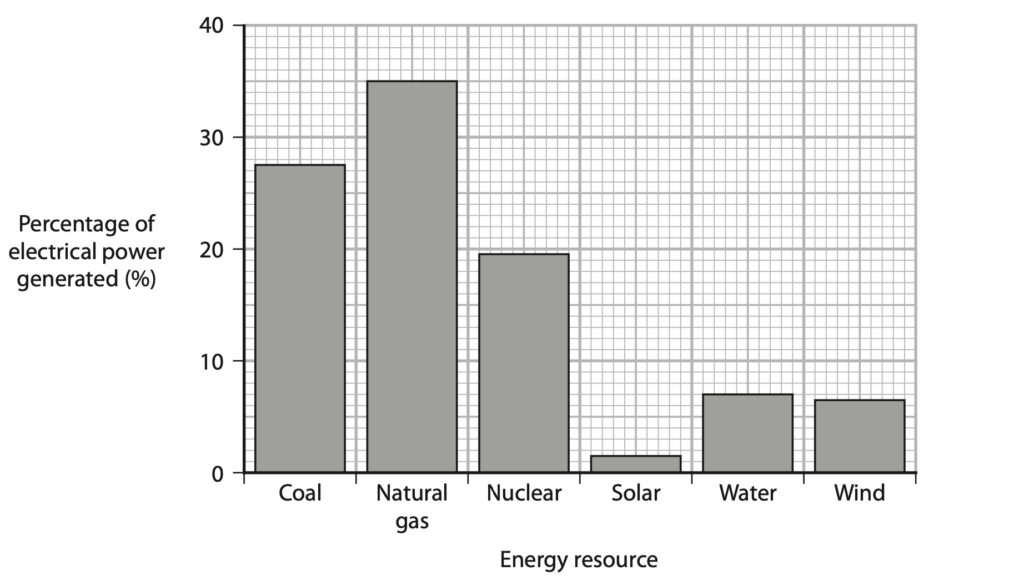
(a) Most of the electricity generated in the USA uses non-renewable energy resources.
(i) State what is meant by the term non-renewable. (1)
(ii) Determine the percentage of electrical power generated using the non-renewable energy resources shown on the bar chart. (2)
percentage = ……………………………………………………..%
(b) In 2018, the USA generated more than half of its electrical power by burning fossil fuels.
Explain one way that burning fossil fuels can be harmful to the environment. (2)
(c) The mean total electrical power output of the USA in 2018 was 4.76×1011W. (i) Calculate the mean electrical power output from solar energy resources. (2)
mean electrical power output = …………………………………………………….. W
(ii) The mean total electrical power output of the USA in 2018 was 4.76×1011W. A typical solar farm generates 250 W of electrical power for every 1.0 m2 of land area used.
Calculate the amount of land area needed if the USA were to generate all of its electrical power using solar energy resources. (2)
land area = …………………………………………………….. m2
(iii) The total land area of the USA is 9.83 × 1012 m2.
Discuss whether the USA could generate all of its electrical power using solar energy resources. (3)
(Total for Question 4 = 12 marks)
January 2021 Paper 1PR Q1
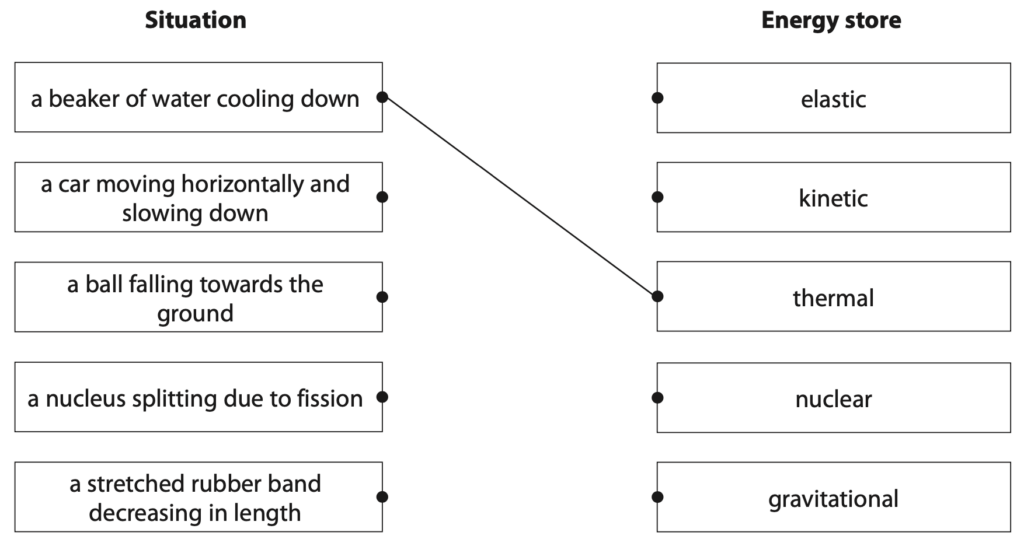
1 (a) The boxes give some situations and some energy stores.
Draw one straight line from each situation to the energy store that decreases for that situation.
The first one has been done for you. (4)
(b) Energy is transferred when a filament lamp is connected to a battery.
(i) Which method of energy transfer takes place between the battery and the lamp?
A electrical
B heating
C mechanical
D radiation
(ii) Which method of energy transfer takes place between the lamp and the surroundings? (1)
A electrical
B light radiation
C mechanical
D sound radiation
(Total for Question 1 = 6 marks)
January 2021 Paper 2PR Q7
7 The diagram shows part of a device used to demonstrate electrostatic charge.
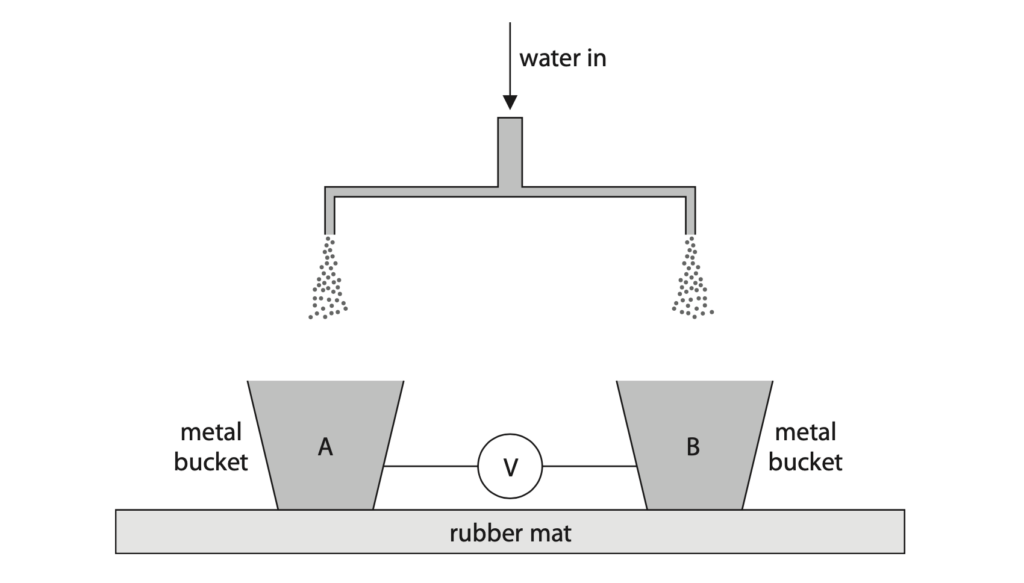
(a) Negatively charged water droplets fall into bucket A. Describe how bucket A becomes negatively charged. (2)
(b) Explain why the negatively charged droplets spread out as they fall. (2)
(c) (i) A droplet hits bucket A with a speed of 3.8 m/s.
Calculate the kinetic energy of the droplet when it hits bucket A. (3)
[mass of droplet = 6.2 × 10–9 kg]
kinetic energy = …………………………………………………….. J
(ii) The total charge stored in bucket A is –1.1 × 10–10 C.
This charge passes through the air between the buckets in 9.2 × 10–3 s,
causing a spark between bucket A and bucket B.
Calculate the mean current between the buckets. (3)
mean current = …………………………………………………….. A
(iii) The spark transfers a charge of –1.1 × 10–10 C.
The mean voltage between the buckets is 1.7 kV.
Calculate the energy transferred by the spark. (3)
energy transferred = …………………………………………………….. J
(Total for Question 7 = 13 marks)
2022 Paper 1P Q8
8 Funcube-1 is a satellite that was launched into orbit around the Earth.
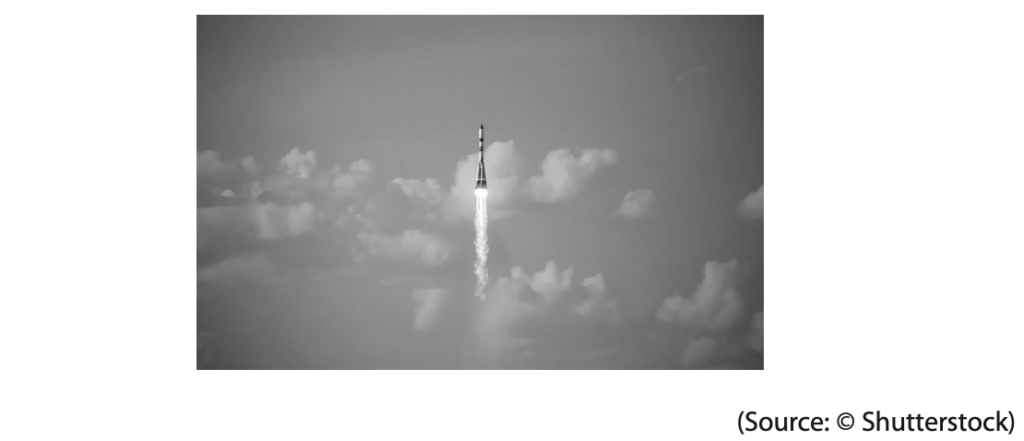

(a) The rocket carrying Funcube-1 burns fuel to accelerate upwards.
As the rocket burns fuel, the energy in its chemical store reduces and the energy in its kinetic store and gravitational store changes.
(i) State how the kinetic store of the rocket changes as the rocket burns fuel. (1)
(ii) State how the gravitational store of the rocket changes as the rocket burns fuel. (1)
(b) The rocket engine stops burning fuel.
The rocket continues to go further away from the surface of the Earth.
The table gives some statements about the rocket’s energy stores.
Add ticks (/) to the table to show which two statements are correct. (2)
| Statement | Correct (/) |
| gravitational store increases | |
| gravitational store stays the same | |
| gravitational store decreases | |
| kinetic store increases | |
| kinetic store stays the same | |
| kinetic store decreases |
(c) Funcube-1 goes into a circular orbit above the surface of the Earth.
(i) State the name of the force responsible for keeping Funcube-1 in orbit. (1)
(ii) Funcube-1 has an orbital radius of 7100 km and an orbital period of 5800 s.
Calculate the orbital speed, in km / s, of Funcube-1. (2)
orbital speed = …………………………………………………….. km/s
(d) Funcube-1 spins and is heated by the Sun.
The diagram shows two coloured metal bars attached to a face of Funcube-1.
The surface of one metal bar is dull and black.
The surface of the other metal bar is shiny and white.
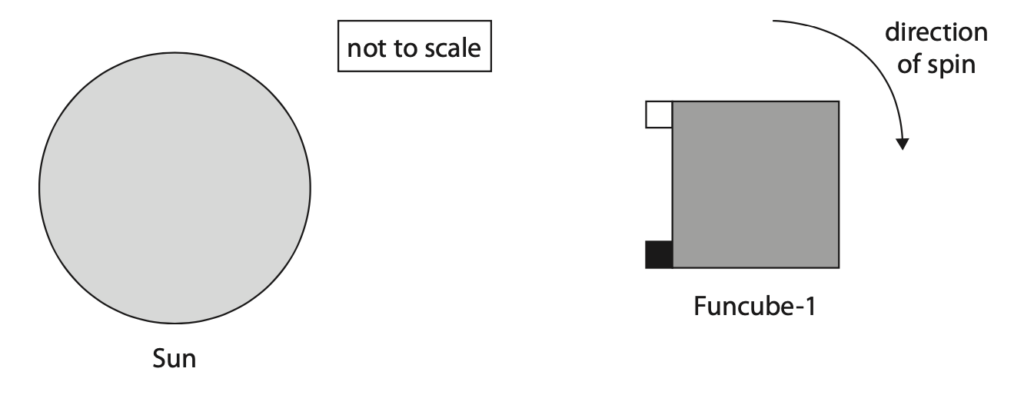
Temperature probes measure the temperature of each metal bar.
Use ideas about thermal energy transfer to explain how the temperature of each metal bar changes as Funcube-1 spins. (4)
(Total for Question 8 = 11 marks)
2022 Paper 1P Q12
(question on energy transfer and magnetism)
12 This question is about an electric fan.
(a) A battery supplies a voltage of 12V and a current of 0.25A to the fan.
The fan is switched on for 12 seconds and the fan gains 25 J in its kinetic energy store.
Calculate the efficiency of this energy transfer. (4)
efficiency = …………………………………………………….. %
(b) The diagram shows part of the electric motor inside the fan.
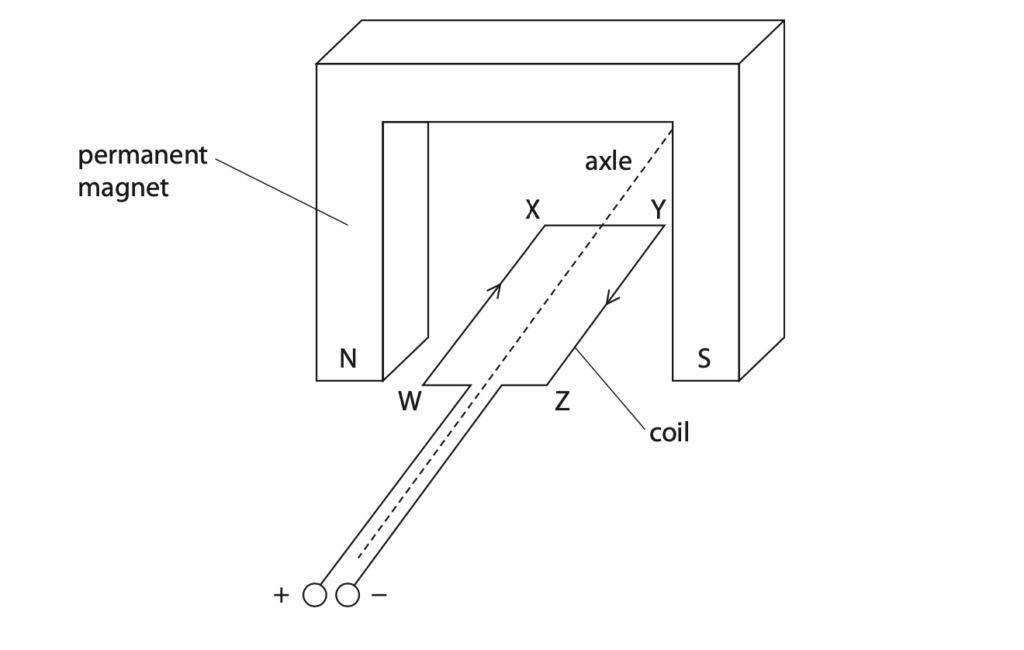
(i) Explain why the coil starts to rotate when there is a current in the coil. (4)
(ii) Which side of the coil moves vertically upwards? (1)
A WX
B XY
C YZ
D ZW
(Total for Question 12 = 9 marks)
2022 Paper 1PR Q5
5 The chart shows the efficiencies of different methods of generating electricity.
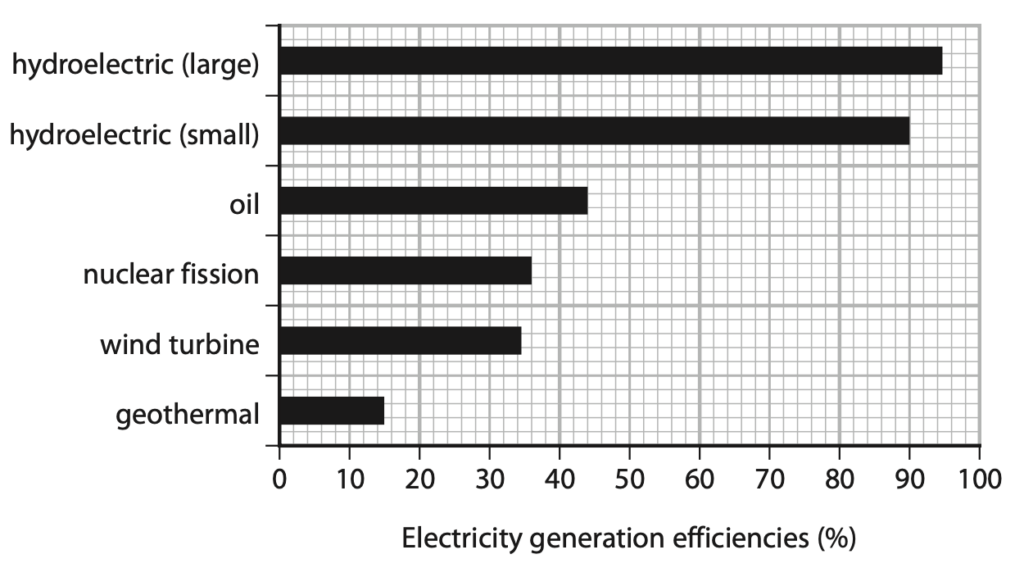
(a) The chart shows that the geothermal power station has an efficiency of 15%.
Explain what is meant by an efficiency of 15%. (2)
(b) A small hydroelectric power station has a useful energy output of 6.0 kJ.
Calculate the total energy input for this power station using information from the chart. (4)
total energy input = …………………………………………………….. kJ
(c) (i) Name a fuel used in the reactor of a nuclear power station. (1)
(ii) These sentences describe the process of nuclear fission.
Complete these sentences by writing a suitable word in each blank space. (5)
A nucleus absorbs a ………………………………………………………………………………… .
The nucleus formed splits because it is ………………………………………………………………………………… .
The nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei called ………………………………………………………………………………… nuclei and two or three ………………………………………………………………………………… .
The energy released is transferred into the ………………………………………………………………………………… energy store of the fission products.
(Total for Question 5 = 12 marks)
2022 Paper 1PR Q12
12 The photograph shows a recyclable box designed for transporting cold food.
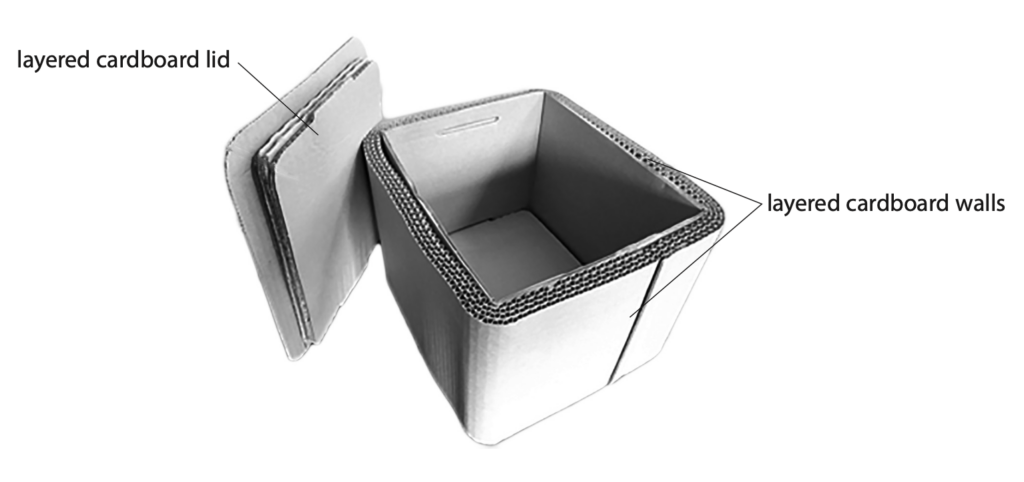

The box has these design features
- thick walls made from several layers of cardboard with air trapped between the layers
- a thick lid made from layers of cardboard
Cold food and ice packs are placed in the box.
(a) Give a reason why there is a net transfer of energy from the outside of the box to the inside of the box during transportation in a hot country. (1)
(b) Explain how the box is designed to reduce energy transfer by conduction. (2)
(c) Explain how the box is designed to reduce energy transfer by convection. (2)
(d) A student suggests that painting the inner surfaces of the box a different colour would help to reduce the rate of energy transfer to the cold food.
Explain which colour the inner surfaces of the box should be painted. (2)
(Total for Question 12 = 7 marks)
2022 Paper 2P Q7
7 The photographs show two large-scale electrical production methods
- a hydroelectric power (HEP) station
- a wind farm
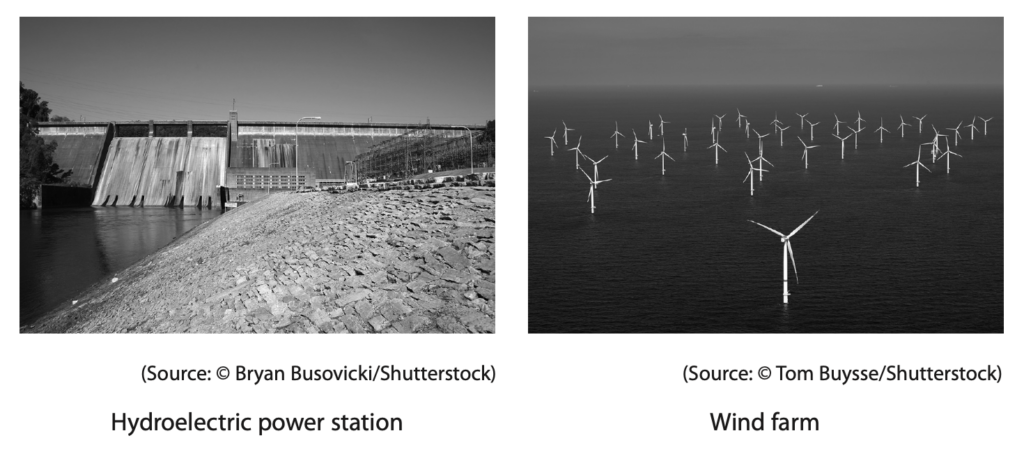

(a) Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using hydroelectric power stations compared with wind farms for large-scale electricity production. (4)
(b) Describe the energy transfers that are involved in generating electricity in a hydroelectric power station. (3)
(Total for Question 7 = 7 marks)
2022 Paper 2P Q9
9 A student uses a small iron nail and a beaker of water to estimate the temperature of a flame. The diagram shows some of the equipment used.
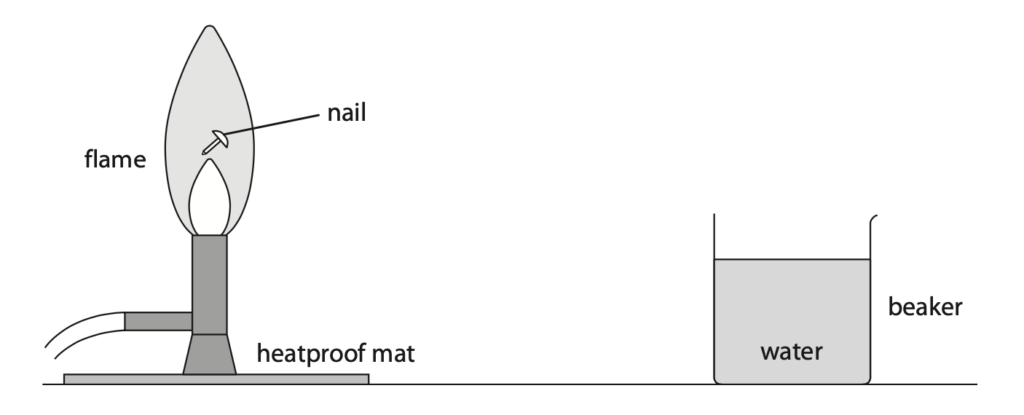
This is the student’s method
- place a thermometer into the beaker of water
- record the temperature of the water
- heat the nail in the flame for a long period of time
- quickly move the nail into the beaker of water
- record the highest temperature of the water
(a) State a safety precaution the student should take. (1)
(b) While in the water, the thermal energy store of the nail decreases and the thermal energy store of the water increases until their temperatures are the same.
The energy lost from the nail is equal to the energy gained by the water.
The table shows the student’s results.
| Mass of water in g | 138 |
| Specific heat capacity of water in J/kg °C | 4200 |
| Temperature change of water in °C | 5.0 |
| Mass of nail in g | 4.8 |
| Specific heat capacity of iron in J/kg °C | 450 |
(i) Show that the energy gained by the water is approximately 3000 J. (2)
(ii) Calculate the temperature change of the nail. (3)
Temperature change = …………………………………………………….. °C
(iii) Give a reason why the calculated temperature change of the nail is lower than the actual temperature change. (1)
(Total for Question 9 = 7 marks)
2022 Paper 2PR Q1
1 (a) The table lists four methods of generating electricity and four energy stores.
| Method of generating electricity | Thermal | Gravitational potential | Kinetic | Chemical |
| Geothermal power station | ||||
| Hydroelectric power station | ||||
| Petrol generator | ||||
| Wind Turbine |
The energy store of the initial energy resource decreases when electricity is being generated.
(i) Complete the table by placing one tick (ü) in each row to show which energy store decreases. (4)
(ii) State which method of generating electricity in the table does not use a renewable energy resource. (1)
(b) State two disadvantages of using wind turbines to generate electricity. (2)
1
2
(Total for Question 1 = 7 marks)
2022 Paper 2PR Q4
(energy resources and energy transfer, electricity and question)
4 A racing car uses an engine and an electric motor to power its wheels.

(a) The electric motor can only operate at maximum power for part of each lap of the race.
The electric motor has a maximum power output of 1.2 × 105 W. The electric motor transfers 4.0 × 106 J of energy when it operates at maximum power.
Calculate the amount of time the electric motor can operate at maximum power. (3)
time = ……………………………………….. s
(b) The diagram shows a simplified view of a direct current (d.c.) electric motor.
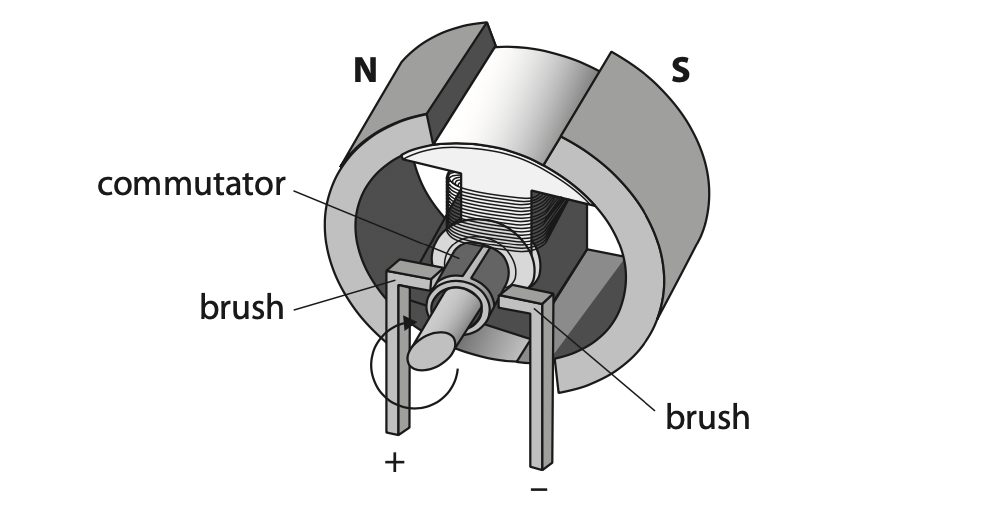
(i) State what is meant by the term direct current. (1)
(ii) Explain the purpose of the brushes and the commutator in the d.c. motor. (3)
(c) The electric motor in the racing car can also be used as a generator to charge a battery pack. It is known as a motor generator unit (MGU).
The rotating wheels of the car cause the magnets in the MGU to spin near a coil of wire.
This induces a current in the coil when the coil is connected to the battery pack.
(i) Name the energy store of the battery pack that increases when the battery pack is being charged. (1)
(ii) Explain why the kinetic energy store of the car must decrease when the MGU charges the battery pack. (3)
(Total for Question 4 = 11 marks)
2022 Paper 2PR Q7
7 A student investigates the rate of cooling of water in a beaker.
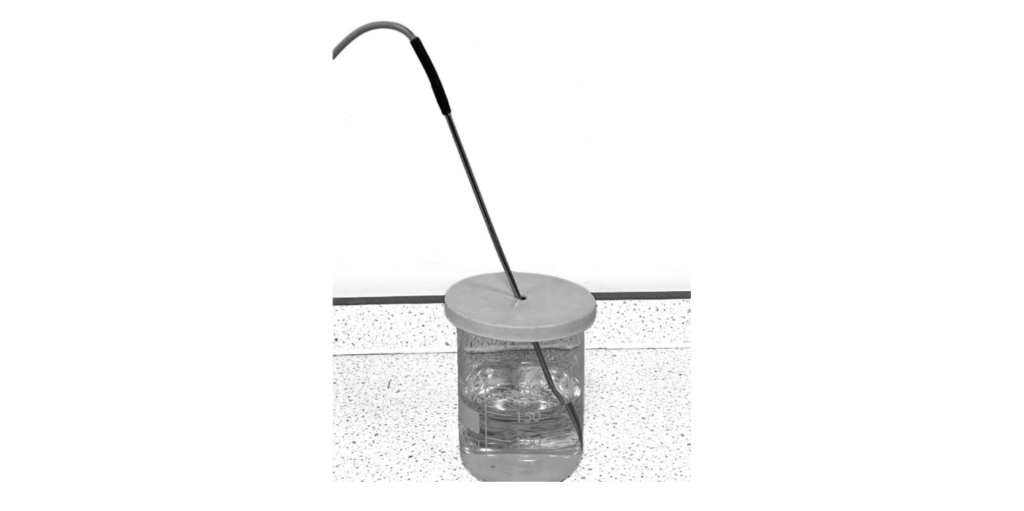

The student pours boiling water into a beaker and monitors the temperature of the water for a period of time.
The graph shows the student’s results.
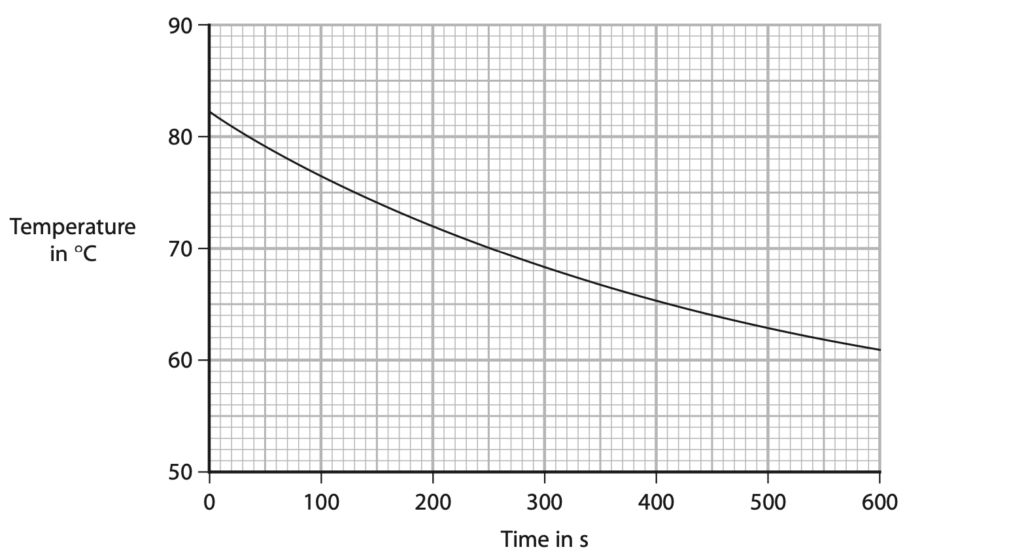
(a) The rate of cooling is represented by the gradient of the graph and is measured in °C/s.
By drawing a tangent to the curve, determine the rate of cooling of the water at 70 °C. (4)
rate of cooling = ……………………………………….. °C/s
(b) The student repeats the investigation with the same beaker wrapped in woollen insulation.

Sketch another line on the graph to show the expected results when the beaker is wrapped in woollen insulation.
Assume that the starting temperature of the water is 82°C. (2)
(Total for Question 7 = 6 marks)










