IGCSE Physics Magnetism & Electromagnetism Past Papers Exam Questions (Edexcel): 2019-20
We analysed the International GCSE past papers and grouped the questions by topic. Here, you will find questions relating to the topic – Magnetism and electromagnetism. Use these to familiarise, practice and prepare for your IGCSE Physics examination.
See IGCSE Physics Past Years Exam Questions from the topic Magnetism and electromagnetism 2021-22 for more questions.
What you need to know
Use the list below as a quick recap for what you need to know before attempting the past year exam questions under this topic. This is based on Edexcel International GCSE in Physics (4PH1) specification with first teaching Sept 2017 and first examination June 2019.
Paper 1 and 2: (6) Magnetism and electromagnetism
Paper 1 covers all the topics except where it is marked “Paper 2 only” while Paper 2 covers all topics.
A. Units
- ampere (A), volt (V) and watt (W)
B. Magnetism
- know that magnets repel and attract each other and attract magnetic substances
- be able to describe the properties of magnetically hard and soft materials
- understand the term magnetic field line
- know that a magnetic field can induce magnetism in some materials
- investigate magnetic field patterns
- how to use two bar magnets to produce a uniform magnetic field
C. Electromagnetism
- know that an electric current in a conductor produces a magnetic field around it
- describe the construction of electromagnets (Paper 2 only)
- draw magnetic field patterns for a straight wire, flat circular coil and solenoid when each is carrying a current (Paper 2 only)
- know that there is a force on a moving charged particle in a magnetic field (Paper 2 only)
- understand why a force is exerted on a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field, and how this effect is applied in dc motors and loudspeakers
- use the left hand rule to predict the direction of the resulting force when a wire carries a current perpendicular to a magnetic field
- describe how the force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field changes with the magnitude and direction of the field and current
D. Electromagnetic Induction
- know that a voltage is induced in a conductor or coil when it moves through a magnetic field or when a magnetic field changes through it and describe the factors that affect the size of the induced voltage
- describe the generation of electricity by the rotation of a coil within a magnetic field or rotating magnet in a coil
(Paper 2 only)
- describe the construction of a transformer, and understand that a transformer changes the size of an alternating voltage. (Paper 2 only)
- explain the use of step-up and step-down transformers in the large scale transmission of electrical energy. (Paper 2 only)
- relationship between input and output voltages and the turns ratio for a transformer. input (primary) voltage/ output (secondary) voltage = primary turns/secondary turns (Paper 2 only)
- relationship input power = output power Vp Ip =Vs Is for 100% efficiency (Paper 2 only)
June 2019 Paper 1 Q2
2. This question is about magnetic fields
(a) Describe an experiment to investigate the magnetic field pattern around a permanent bar magnet.
You may draw a diagram to help you answer. (3)
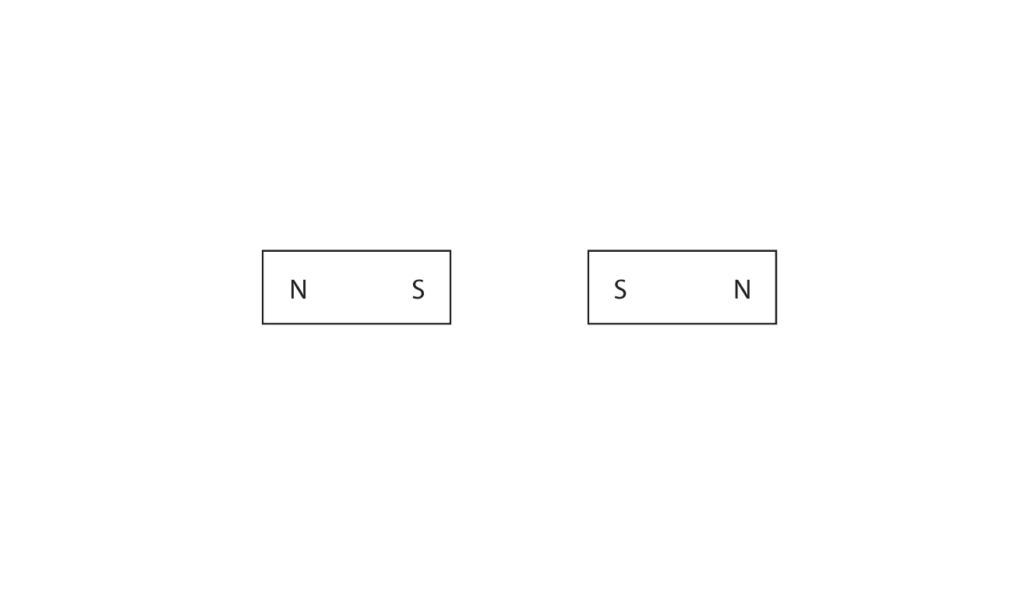
(b) The diagram shows two bar magnets.
Complete the diagram to show the magnetic field pattern. (3)
June 2019 Paper 1PR Q11
11 A student investigates the magnetic fields produced by magnets.
(a) Describe a method he could use to determine the shape and direction of the magnetic field produced by a bar magnet.
You may use a diagram to help your answer. (3)
(b) The diagram shows the shape of the magnetic field around the bar magnet.
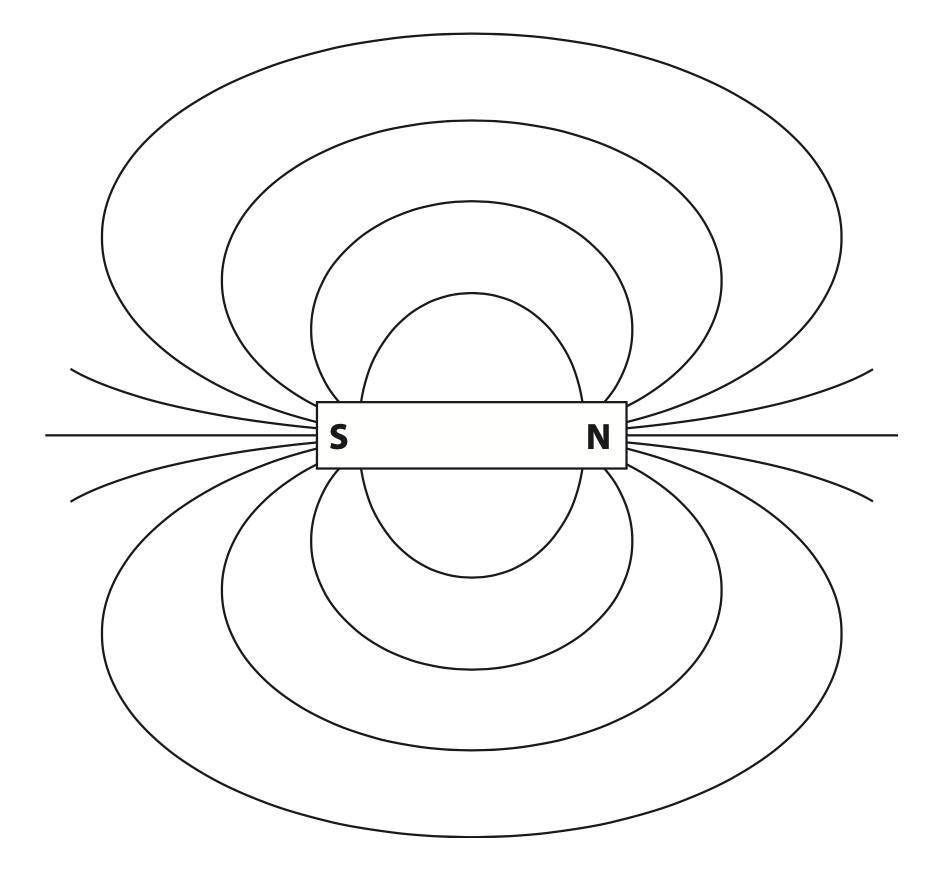
(i) Add two arrows to the diagram to show the direction of the magnetic field. (1)
(ii) Explain how the diagram shows that the strength of the magnetic field changes. (2)
(c) Magnetic field strength can be measured in units of milli-tesla (mT).
A student uses a different magnet.
The student measures the magnetic field strength at different distances from the north pole of this magnet.
The graph shows his results.
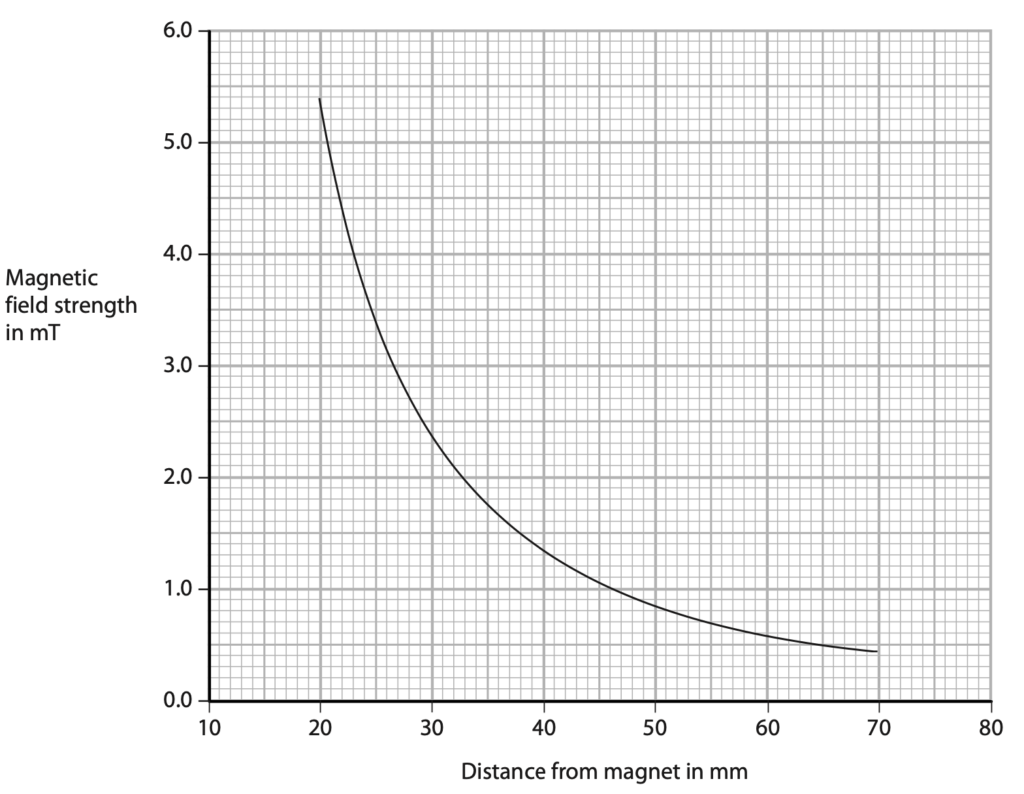
The student concludes that his results obey this relationship.
magnetic field strength × distance2 = constant
Use data from the graph to deduce whether the student’s results support this conclusion. (4)
Total for Question 11 = 10 marks
June 2019 Paper 2PR Q6
6 A student investigates transformers.
(a) The diagram shows a typical transformer.
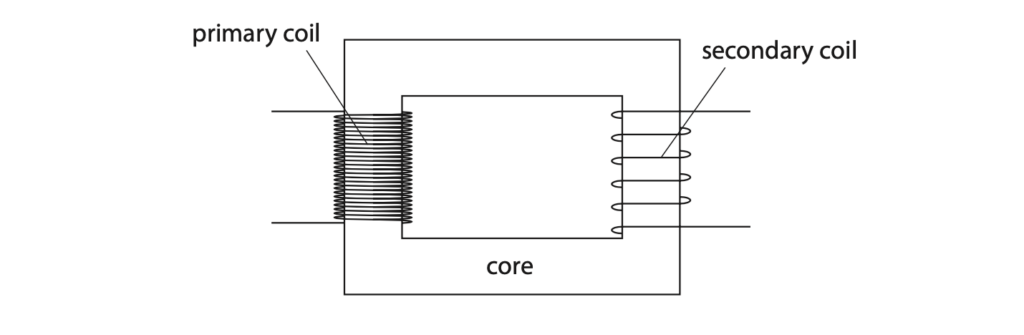
State the name given to this type of transformer. (1)
(b) The student investigates the effect of changing the number of turns in the secondary coil.
This is his method.
- apply a constant maximum voltage to a primary coil with 1200 turns
- use a secondary coil with 100 turns
- measure the output voltage of the transformer
- replace the secondary coil with one that has 200 turns
- measure the output voltage again
The student repeats this method using different numbers of turns in the secondary coil.
(i) Suggest how the student could improve the reliability of his investigation. (1)
(ii) These are the student’s results.
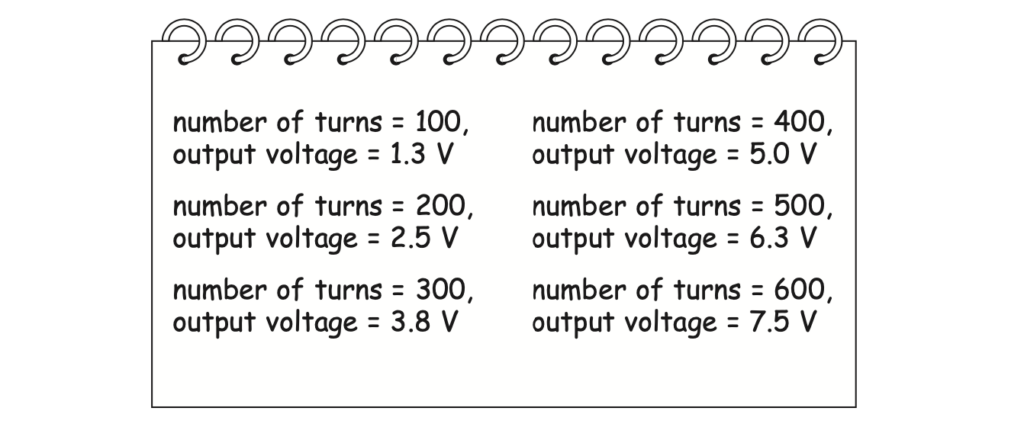
Draw a table of these results. (3)
(iii) Suggest how the student could improve the precision of his voltage measurement. (1)
(c) The student plots this graph to show the results of his investigation.
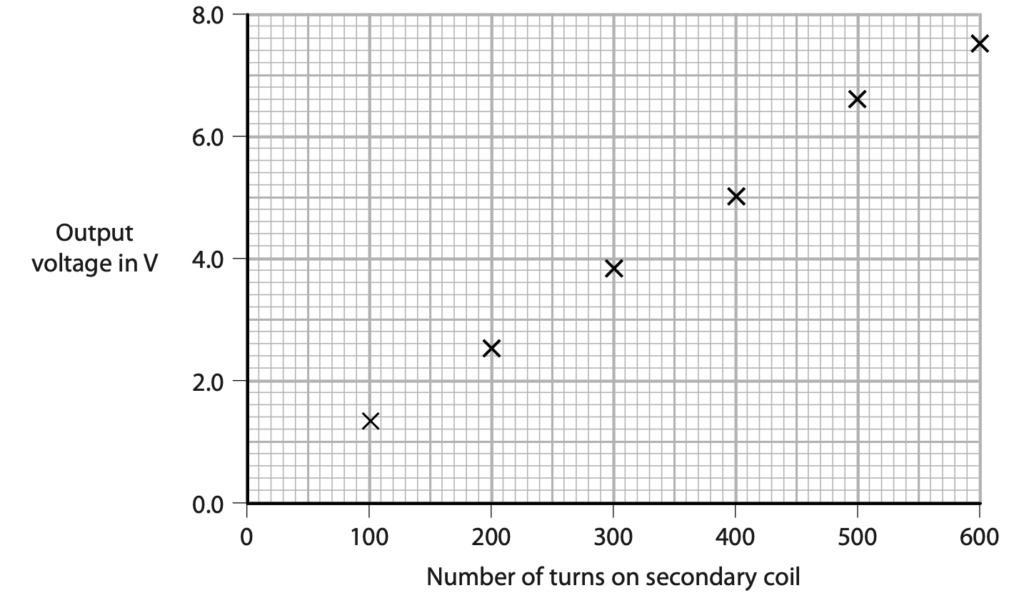
(i) The student plots one of his results incorrectly.
Draw a circle around the incorrectly plotted result on the graph. (1)
(ii) Draw the line of best fit. (1)
(iii) Describe the relationship shown by the graph. (2)
(d) The primary coil has 1200 turns.
Using the student’s data, calculate the primary voltage used in his investigation. (4)
primary voltage = ……………………………………….. V
(Total for Question 6 = 14 marks)
January 2020 Paper 1 Q1
1 The passage describes some of the properties of magnets and magnetic fields.
Use words from the box to complete the passage.
| aluminium | copper | hard |
| negative | north | positive |
| soft | south | steel |
Each word may be used once, more than once or not at all. (5)
The north pole of one magnet will repel the …………………………………………………….. pole of another magnet.
There is attraction between …………………………………………………….. and magnets.
Materials that are difficult to magnetise are called …………………………………………………….. magnetic materials.
The direction of the magnetic field lines for a magnet is from …………………………………………………….. to south.
Iron is a …………………………………………………….. magnetic material.
Total for Question 1 = 5 marks
January 2020 Paper 1PR Q12
12 Diagram 1 shows some apparatus used to demonstrate the magnetic force on a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field.
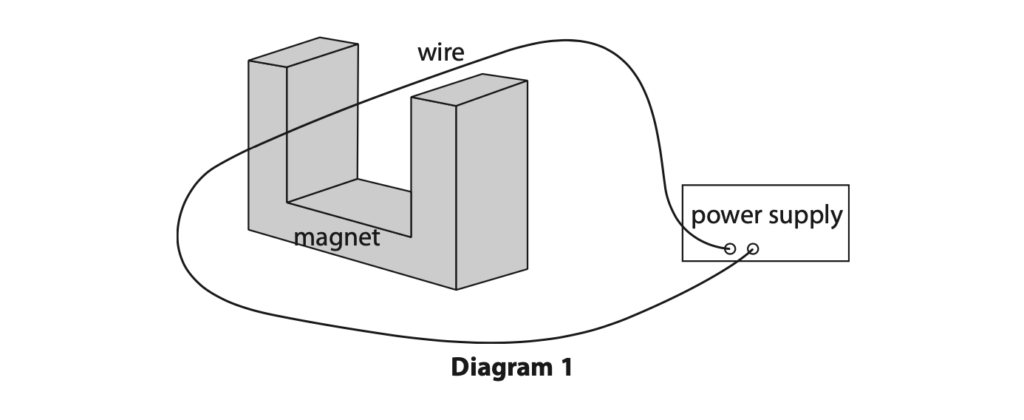
(a) Diagram 2 shows four different arrangements of the apparatus.
The symbol
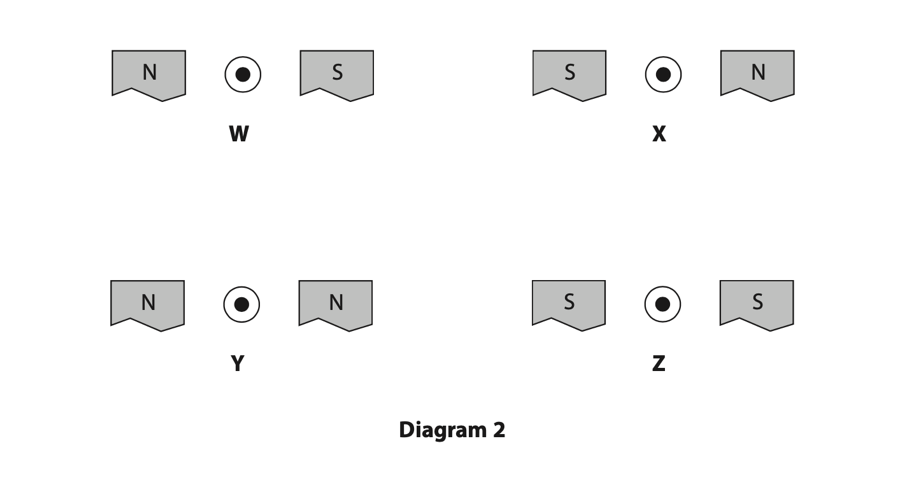
Which arrangement of the apparatus will cause there to be an upwards magnetic force on the wire? (1)
A W
B X
C Y
D Z
(b) The wire has a mass of 6.5 g.
(i) Calculate the weight of the wire. (2)
Give your answer in mN.
weight = …………………………………………………….. mN
(ii) There is an upwards magnetic force of 34 mN acting on the wire.
Calculate the acceleration of the wire. (5)
acceleration = …………………………………………………….. m/s2
(iii) Explain one method of increasing the magnitude of the magnetic force on the wire (2)
(iv) Explain how the circuit could be changed to make the wire vibrate. (2)
(Total for Question 12 = 12 marks)
January 2020 Paper 2P Q8
8 This question is about magnetic fields.
(a) Diagram 1 shows a positively charged proton moving downwards in a uniform magnetic field.
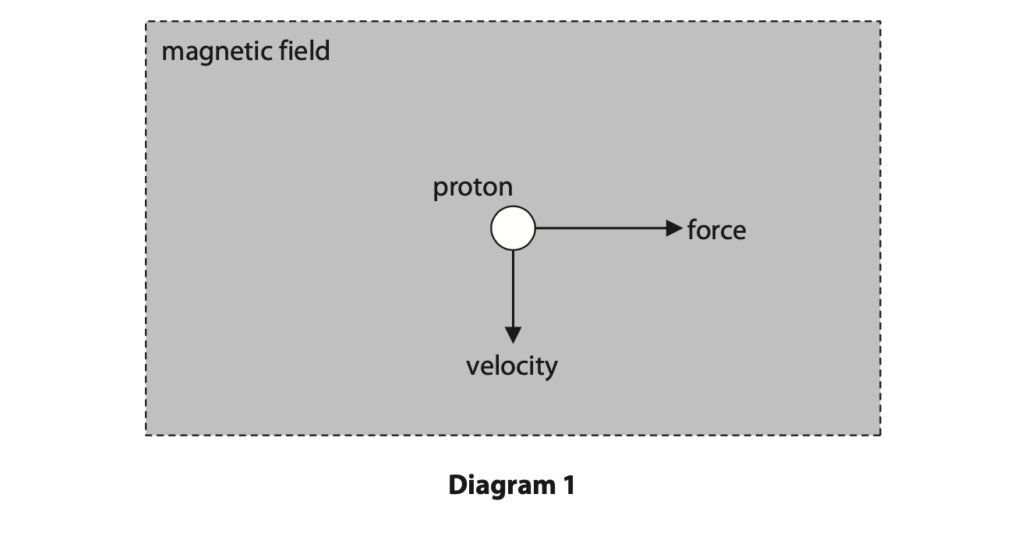
The proton experiences a force to the right.
What is the direction of the magnetic field? (1)
A into the page
B left
C out of the page
D upward
(b) When a current passes through a flat circular coil, a magnetic field is produced. Complete diagram 2 by drawing the magnetic field of the flat circular coil. (3)
(c) A wireless charging base uses a magnetic field to charge the battery of a mobile phone.

There is an alternating current in a coil of wire in the charging base.
There is another coil of wire connected to the battery in the mobile phone.
(i) Explain how the wireless charging base charges the battery of the mobile phone. (3)
(ii) Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using a high current in the wireless charging base. (2)
(Total for Question 8 = 9 marks)
January 2020 Paper 2PR Q1
1 This question is about electromagnetic (EM) waves.
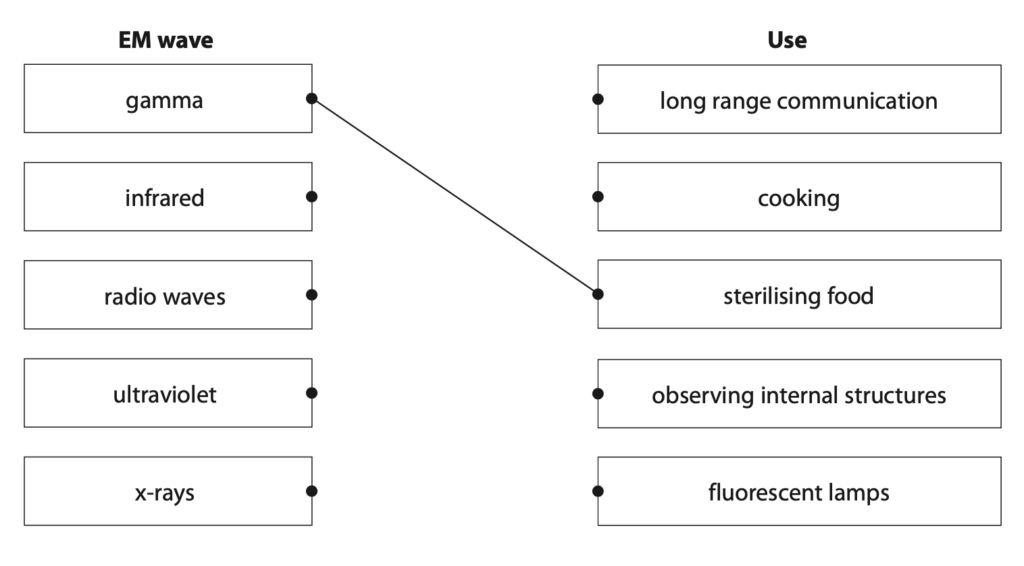
(a) The boxes show some EM waves and their uses.
Draw one straight line from each EM wave to its correct use. One has been done for you. (3)
(b) Which of these is a hazard of microwave radiation? (1)
A blindness
B cell mutation
C internal heating of tissue
D skin burns
(c) State the name of an electromagnetic wave with a wavelength longer than microwave radiation. (1)
(Total for Question 1 = 5 marks)
January 2020 Paper 2PR Q6
6 The diagram shows the first stages in a method of transferring energy electrically through long distances.
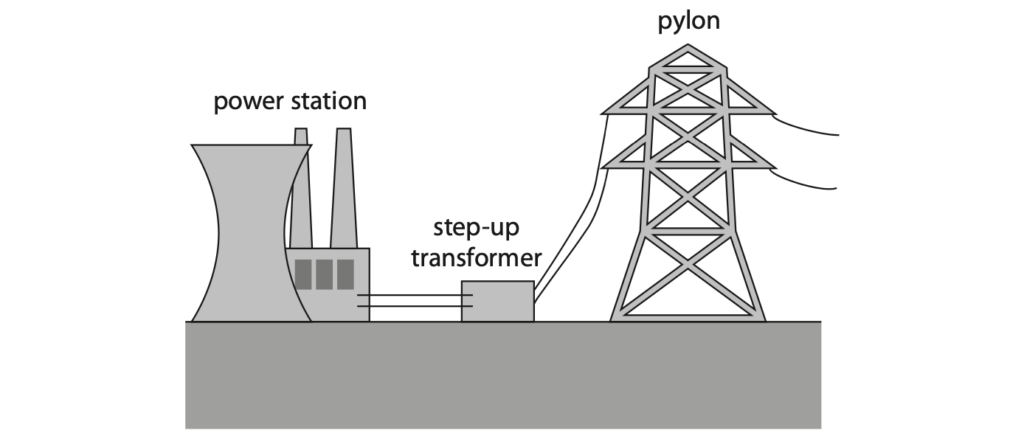
The table shows data about the step-up transformer.
| number of turns in primary coil | 2600 |
| input voltage in kV | 15 |
| output voltage in kV | 330 |
(a) (i) State the formula linking input voltage, output voltage, number of primary turns and number of secondary turns for a transformer. (1)
(ii) Calculate the number of turns on the secondary coil. (3)
(b) Explain why step-up and step-down transformers are used in the large-scale transmission of electricity.
You may draw a diagram to support your answer. (4)
(Total for Question 6 = 8 marks)
January 2020 Paper 2PR Q7
7 This question is about a proton moving in a uniform magnetic field.
(a) Describe how to use two permanent magnets to produce a uniform magnetic field.
You may draw a diagram to support your answer. (2)
(b) The diagram shows a proton moving in a circular path at constant speed in a uniform magnetic field.
This motion is similar to the movement of a planet in the Solar System.
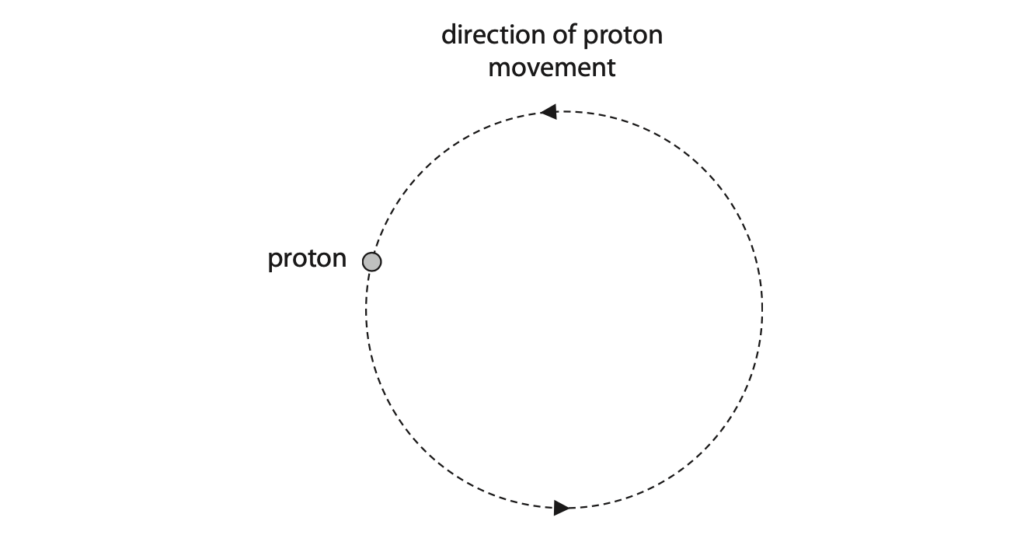
(i) Draw an arrow to show the direction of the force on the proton. (1)
(ii) Accurately measure the diameter of the proton’s path. (2)
diameter = ………………………………………. cm
(iii) The proton completes one orbit of its circular path in a time period of 8.7 × 10–6 seconds.
Calculate the orbital speed of the proton. (3)
orbital speed = ………………………………………. m/s
(Total for Question 7 = 8 marks)
June 2020 Paper 1P Q9
9 This question is about a radio powered by a person turning a handle.
The radio has a battery which stores energy when the handle is turned.
(a) The diagram shows the part of the radio called a generator.
The generator produces a voltage which does electrical work on the battery.
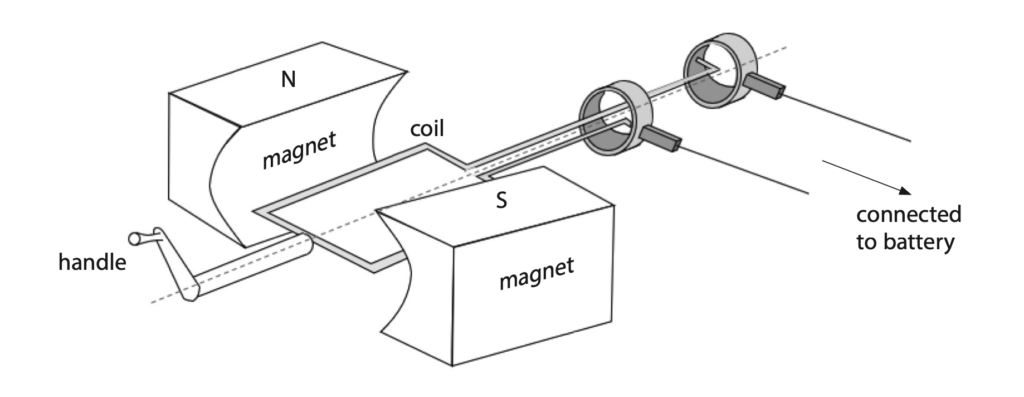
Explain how the generator produces a voltage. (3)
(b) The radio receives a radio wave of frequency 93 MHz.
(i) State the formula linking speed, frequency and wavelength of a wave. (1)
(ii) Calculate the wavelength of the radio wave. (3)
[speed of radio waves = 3.0 × 108 m/s]
wavelength = ………………………………………… m
(c) The signal received by the radio is converted into an alternating current (a.c.) signal.
(i) Describe how the loudspeaker in the radio converts this a.c. signal into a sound wave. (4)
(ii) State a modification that would increase the force on the loudspeaker coil. (1)
(Total for Question 9 = 12 marks)
June 2020 Paper 1PR Q10
10 This question is about bar magnets.
(a) Describe an investigation to show the shape and direction of the magnetic field for a bar magnet.
You may draw a diagram to help your answer. (3)
(b) A bar magnet is used in a bicycle dynamo.
The diagram shows a cross-section of a bicycle dynamo.
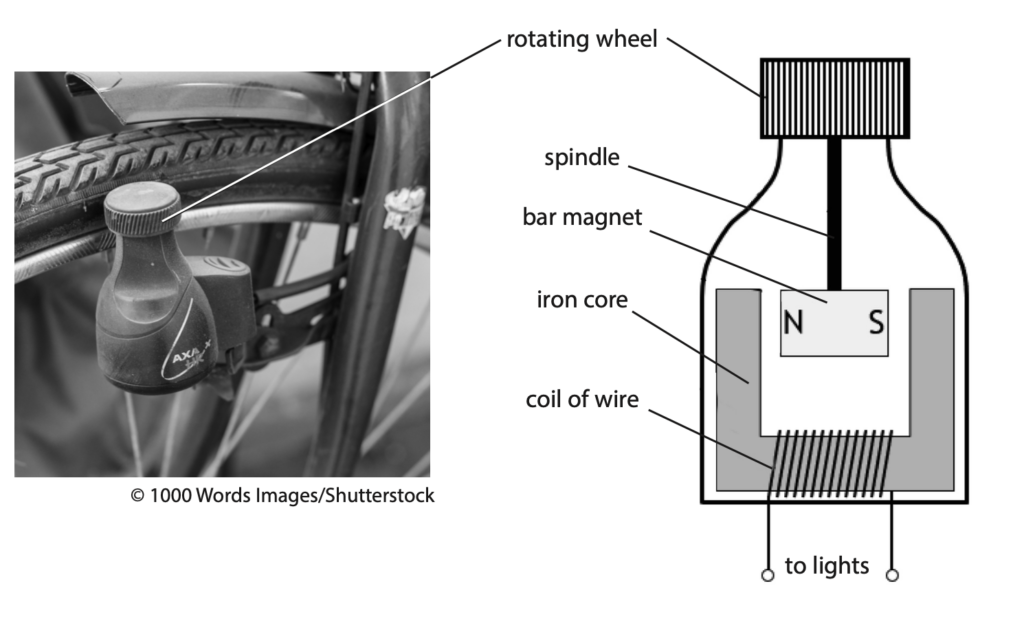
The dynamo has a rotating wheel that presses against the tyre of the bicycle.
The rotating wheel is connected to a bar magnet by a spindle.
When the rotating wheel spins, the bar magnet spins.
(i) The dynamo is connected to the lights on the bicycle.
Explain how the dynamo causes the lights to turn on when the bicycle is moving. (4)
(ii) Suggest a disadvantage of using the dynamo to power the bicycle lights. (1)
(Total for Question 10 = 8 marks)
June 2020 Paper 2P Q7
7 Diagram 1 shows a loop of wire connected to a power supply.
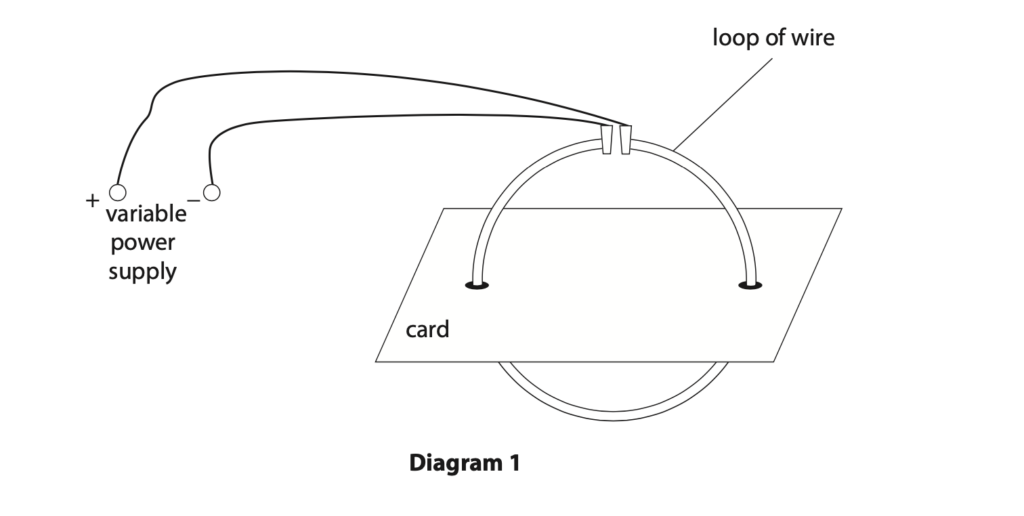
(a) Describe how to find the shape of the magnetic field produced by the loop of wire. (3)
(b) Diagram 2 shows the view from above the card with two cross-sections of the loop of wire.
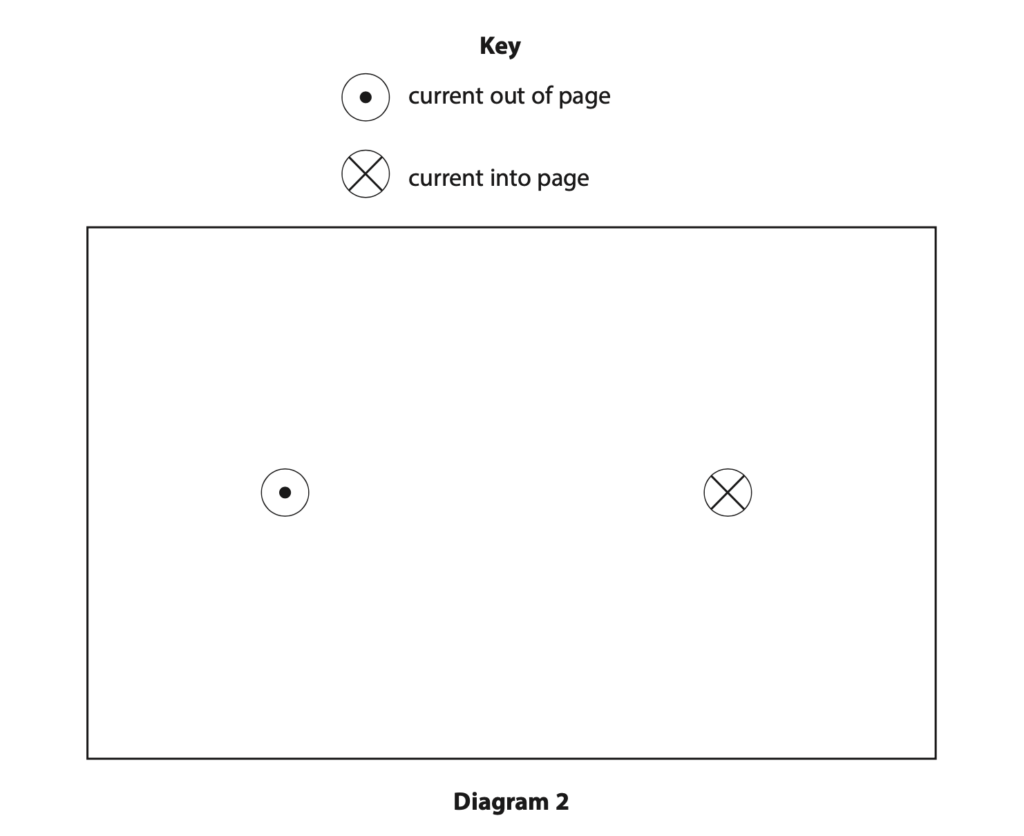
On diagram 2, draw the magnetic field produced by the two cross-sections of the loop of wire. (4)
(c) (i) These diagrams show the magnetic field acting on a cross-section of wire when the current in the wire is out of the page. (2)
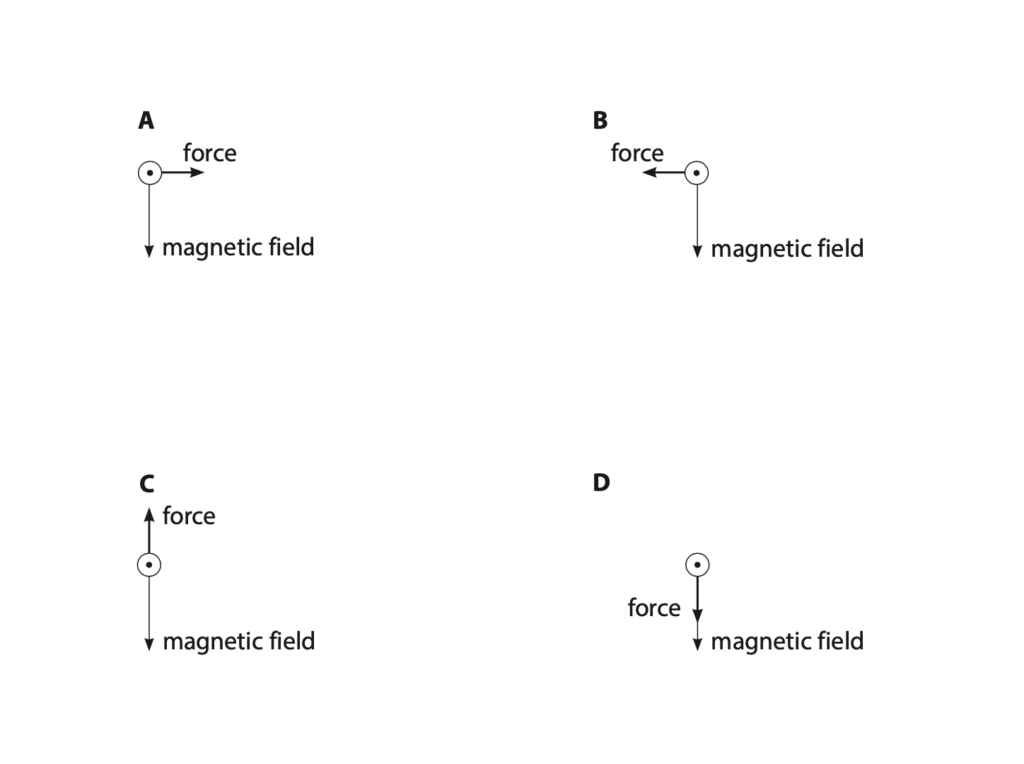
Which diagram shows the correct direction of the force acting on the cross-section of wire due to the magnetic field? (1)
A
B
C
D
(ii) The magnetic field acting on the cross-section of wire is produced by the current in the other side of the loop of wire.
Explain why there is no effect on the direction of the force on the cross-section of wire when the direction of the current in the loop is reversed. (2)
(Total for Question 7 =10 marks)
June 2020 Paper 2P Q8
8 Welding is a process where pieces of metal are melted and then joined together.
The diagram shows apparatus used for welding.
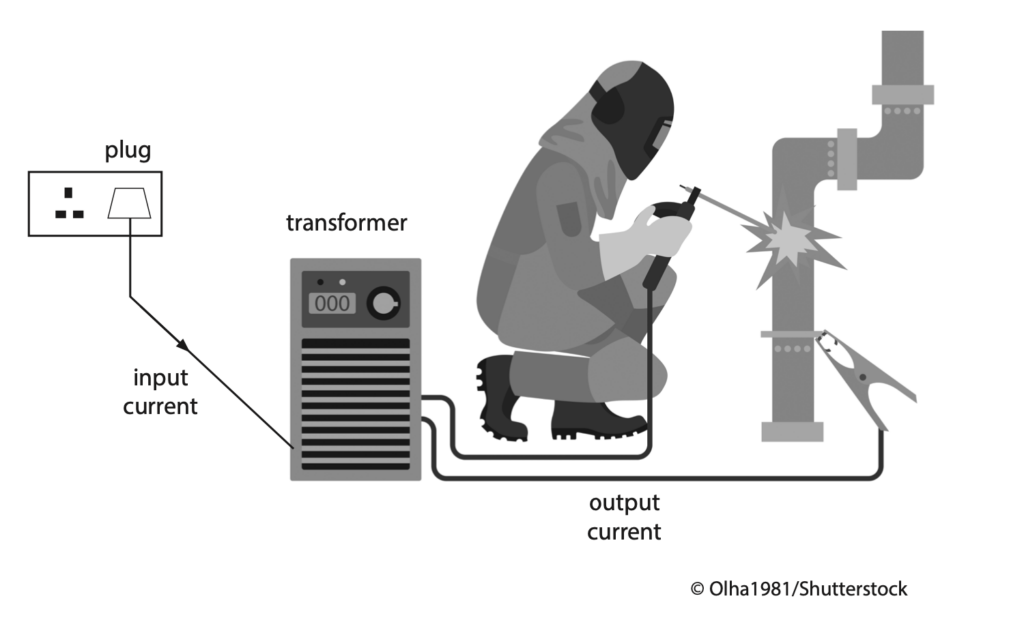
The welding apparatus uses the transformer to decrease the voltage from 230 V.
(a) State the name of this type of transformer. (1)
(b) State the formula linking the turns ratio, the input voltage and the output voltage
for a transformer. (1)
(c) The table gives some information about the transformer.
| input voltage in V | 230 |
| number of turns on input coil | 16 |
| number of turns on output coil | 4 |
| input current in A | 11 |
(i) Use information from the table to calculate the output current of the transformer. (5)
Assume that the transformer is 100% efficient.
current = ……………………….. A
(ii) A fuse is installed in the plug which supplies the input current.
Which fuse should be used in this plug? (1)
A 3A
B 5A
C 10A
D 13A
(Total for Question 8 = 8 marks)










