IGCSE Physics Past Years Exam Questions: Energy Resources and Energy Transfer 2023-24
We analysed the International GCSE past papers and grouped the questions by topic. Here, you will find questions relating to the topic – Energy resources and energy transfers. Use these to familiarise, practice and prepare for your IGCSE Physics examination.
You can find earlier papers below:
- IGCSE Physics Past Years Exam Questions on Energy resources and energy transfers 2019-20.
- IGCSE Physics Past Years Exam Questions on Energy resources and energy transfers 2021-22.
What you need to know
Use the list below as a quick recap for what you need to know before attempting the past year exam questions under this topic. This is based on Edexcel International GCSE in Physics (4PH1) specification with first teaching Sept 2017 and first examination June 2019.
Paper 1 and 2: (4) Energy resources and energy transfers
Paper 1 covers all the topics except where it is marked “paper 2 only” while Paper 2 covers all topics.
A. UNITS
- kilogram (kg), joule (J), metre (m), metre/second (m/s), metre/second2 (m/s2), newton (N), second (s) and watt (W)
B. ENERGY TRANSFERS
- describe energy transfers from one energy store to another. Energy stores: chemical, kinetic, gravitational, elastic, thermal, magnetic, electrostatic, nuclear. Energy transfers: mechanical, electrical, heating, radiation (light and sound).
- principle of energy conservation.
- relationship between efficiency, useful energy output and total energy input. efficiency=useful energy transferred (output)/total energy supplied (input) ×100%
- describe a variety of everyday and scientific devices and situations for the transfer of the input energyincluding their representation by Sankey diagrams.
- describe how thermal energy transfer may take place by conduction, convection and radiation.
- explain the role of convection in everyday phenomena.
- explain how emission and absorption of radiation are related to surface and temperature.
- investigate thermal energy transfer by conduction, convection and radiation.
- explain ways of reducing unwanted energy transfer such as insulation
C: WORK AND POWER
- relationship between work done, force and distance moved in the direction of force. W=F×d
- work done is equal to energy transferred.
- use the definitions of work and power.
- the relationship for gravitational potential energy, mass, gravitational field strength and height. GPE = m × g × h
- the relationship for kinetic energy. kinetic energy = 1/2 × mass × speed2 (KE = 1/2 ×m×v2)
- how conversation of energy produces a link between gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy and work.
- describe power as rate of transfer of energy or the rate of work
- relationship between power, work done (energy transferred) and time. P = W/t
(paper 2 only)
D. ENERGY RESOURCES AND ELECTRICITY GENERATION
- describe the energy transfers involved in generating electricity (wind, water, geothermal, solar heating, solar cells, fossil fuels, nuclear)
- describe the advantages and disadvantages of large-scale electricity production from various renewable and non-renewable resources.
January 2023 Paper 1P Q3
3. A winch is used to pull a truck along a horizontal road. The winch is connected to the truck by a thick rope.

(a) The winch does 41 kJ of useful work on the truck when the truck is pulled a horizontal distance of 15 m.
(i) State the formula linking work done, force and distance moved in the direction of the force. (1)
(ii) Calculate the force that the rope exerts on the truck. (3)
force = …………………………………………………….. N
(b) The winch includes a small engine. The engine burns petrol to power the motor in the winch.
The winch transfers energy mechanically to the truck.
(i) The winch has an efficiency of 25% when pulling the truck.
Draw a Sankey diagram for this energy transfer. (3)
(ii) The winch can also be used to pull the truck uphill at a constant speed. The table gives some energy stores.
Add one tick (/) to each row to show what happens to the energy in each store as the truck is pulled uphill. (4)
| Energy store | Decreases | Increases | Stays the same |
| chemical store of petrol in winch | |||
| gravitational store of truck | |||
| kinetic store of truck | |||
| thermal store of surroundings |
(Total for Question 3 = 11 marks)
Jan 2023 Paper 1P Q10
10 A student pours a known volume of hot water into a metal container. They place the metal container into an insulated plastic cup containing an equal volume of cold water.
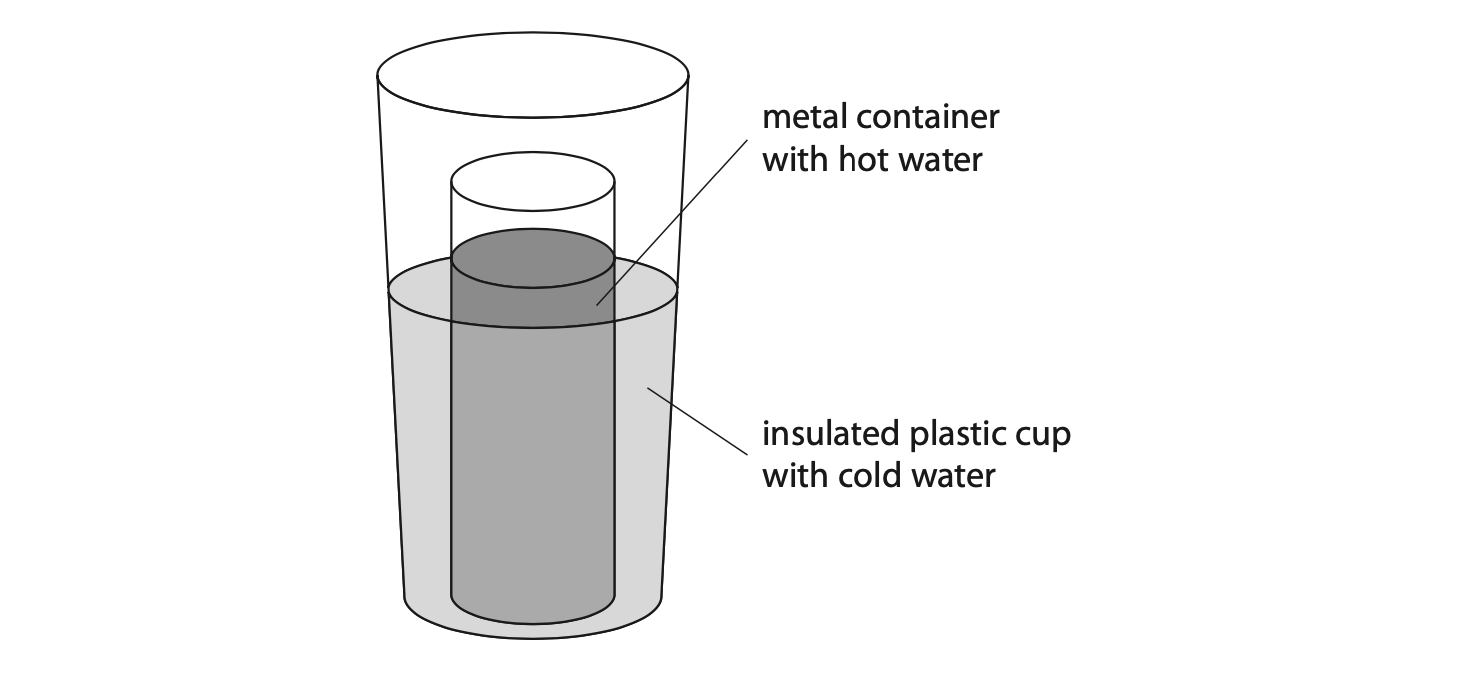
The student uses temperature probes to measure the temperatures of both the water in the metal container and the water in the plastic cup.
The hot water has an initial temperature of 70 °C and the cold water has an initial temperature of 5 °C.
(a) On the axes, sketch how the temperature of the hot water and the temperature of the cold water vary with time. (4)
(b) Explain why the temperatures of the hot water and the cold water change. You should refer to different types of thermal energy transfer in your answer. (4)
(c) Explain how placing a lid on the plastic cup would affect the results. (3)
(Total for Question 10 = 11 marks)
January 2023 Paper 1PR Q6
6 The diagram shows a small computer in two difference cases, X and Y.
The electronic chip in the computer is hot when in use. Each case is designed to cool the computer chip.
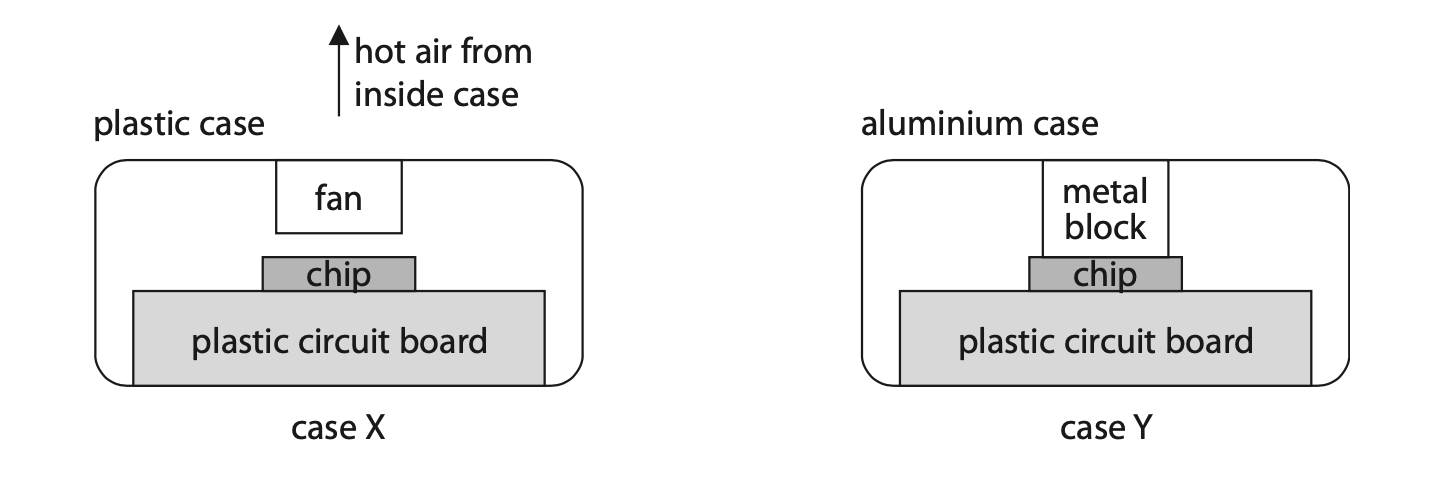
Case X is made of white plastic and has a fan.
Case Y is made of black-painted aluminium metal and has no fan. There is a metal block that is in contact with the case and the chip.
(a) Explain the main method of heat transfer from the chip to the surroundings for case X. (3)
(b) Explain the main method of heat transfer from the chip to the surroundings for case Y. (3)
(c) (i) State the formula linking power, current and voltage. (1)
(ii) The small computer operates at a voltage of 5.1 V with a current of 2.9 A.
Calculate the power of the small computer.
Give the unit. (3)
power = …………………………………………………….. unit ……………………………………………………..
(Total for Question 6 = 10 marks)
January 2023 Paper 2P Q1
1 The photograph shows a person using a roll of plastic wrapping to cover a plate of food.
The plastic wrapping sticks to the plate due to electrostatic charges.

The passage explains why the plastic wrapping sticks to the plate.
Use words from the box to complete the passage.
Each word may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
| attract | electrons | negative | Neutral |
| neutrons | positive | protons | repel |
The person pulls a layer of plastic wrapping from the roll.
Forces between the layers of wrapping transfer particles called …………………………………………………….. from one layer to another layer.
The layer gaining these particles acquires a …………………………………………………….. charge.
The layer losing these particles acquires a …………………………………………………….. charge.
The negatively charged layer of wrapping repels …………………………………………………….. in the plate, leaving a positive charge in the plate where it touches the plastic wrapping.
The wrapping and plate …………………………………………………….. due to them having opposite charges.
(Total for Question 1 = 5 marks)
Jun 2023 Paper 1P Q3
Question 3
A family has a television set.
(a) The television set has a low power mode called standby.
When on standby, the power rating of the television set is 0.27W.
Calculate the energy transferred to the television set on standby in 12 hours. (3)
energy transferred = …………………………………………………….. J
(b) In normal use, the current in the television set is 0.31 A.
(i) Explain how a fuse works to protect the television set if there is a fault. (3)
(ii) Explain why a 13 A fuse is not an appropriate choice of fuse to use in the plug of this television set. (2)
(Total for Question 3 = 8 marks)
June 2023 Paper 1P Q8
8 In some countries, snow can fall and collect on the ground.
Diagram 1 shows that after the snow has fallen, the sky can be clear, leaving the snow directly exposed to the Sun.

(a) Explain why the white snow will take a long time to melt, even though directly exposed to the Sun. (2)
(b) Diagram 2 shows a different piece of ground that has a metal drain cover. If the snow lands on metal, the snow takes a shorter time to melt.
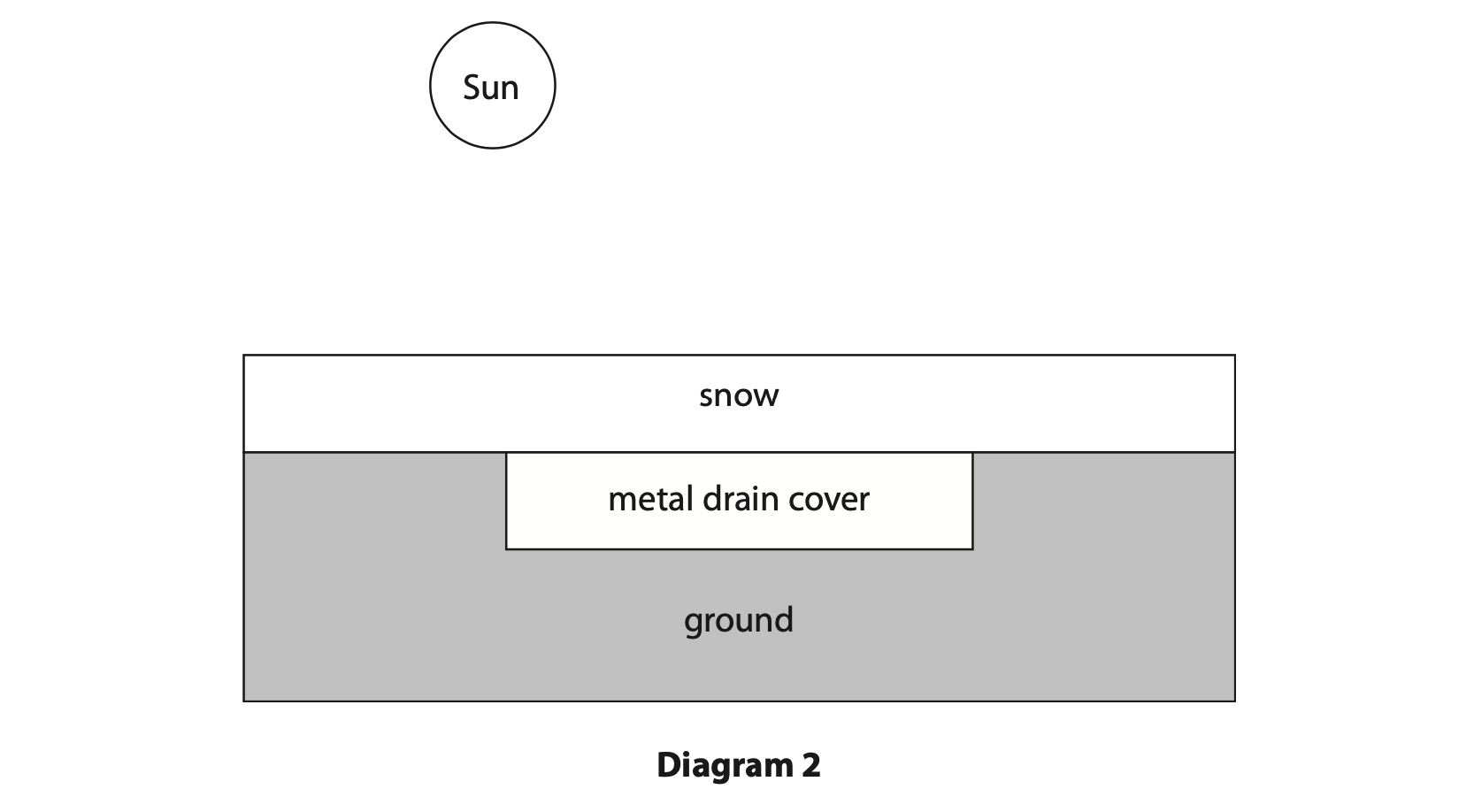
Explain why the snow melts in a shorter time on the metal drain cover. (2)
(c) Explain how a convection current above the snow increases the time taken for the snow to melt. (2)
(Total for Question 8 = 6 marks)
June 2023 Paper 1PR Q3
3. A model electric motor is used to lift a load through a vertical height.
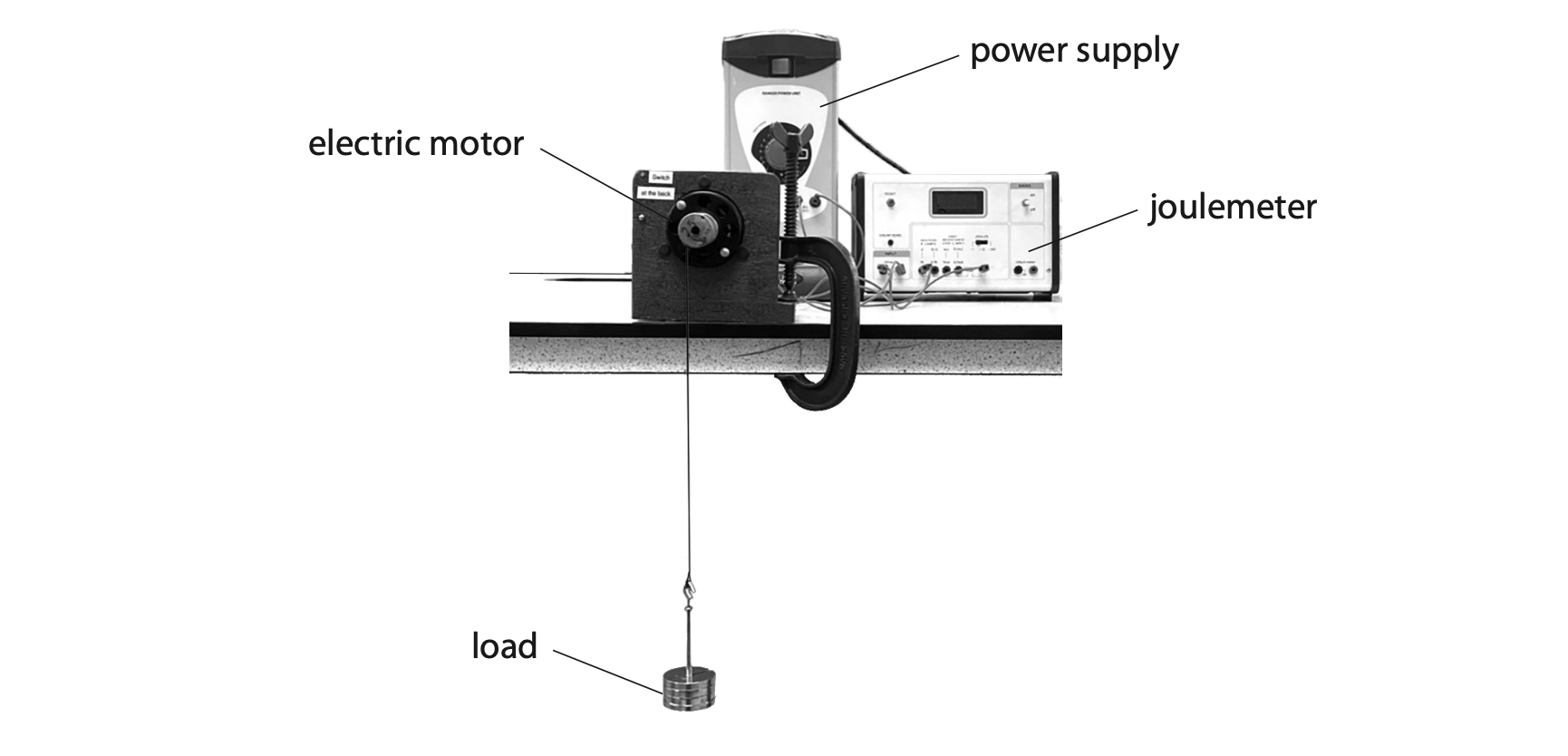
(a) The load has a mass of 400 g and gains 3.2 J of energy in its gravitational store when lifted.
(i) State the formula linking gravitational potential energy, mass, gravitational field strength (g) and height. (1)
(ii) Calculate the height the load is lifted. (3)
height = …………………………………………………….. m
(iii) State the amount of useful work done on the load by the motor when the load is lifted through this height. (1)
work done = …………………………………………………….. J
(b) The load is lifted at a constant speed.
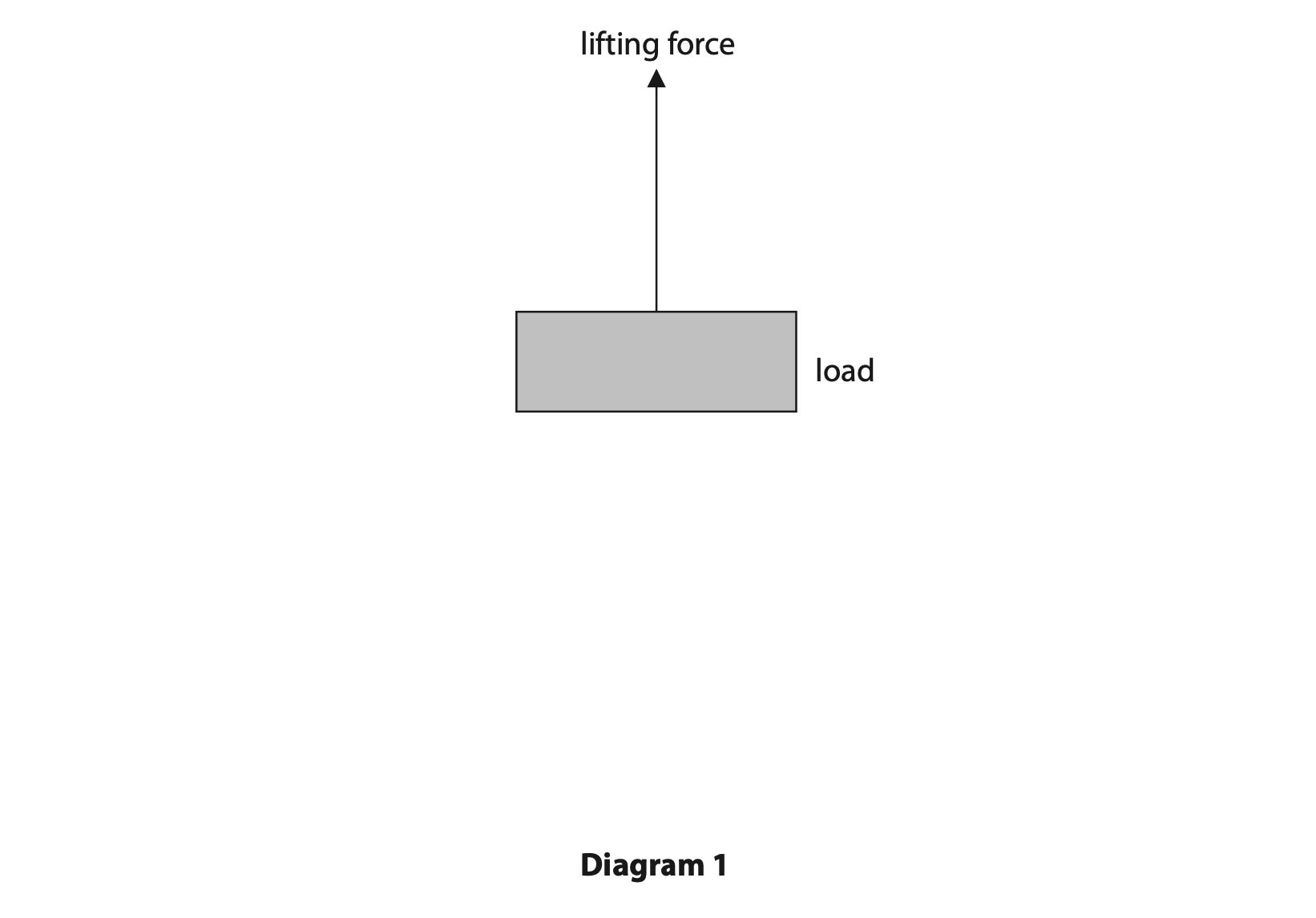
Diagram 1 shows the lifting force acting on the load as it is lifted.
Draw a labelled arrow on diagram 1 to show the other force acting on the load.
Ignore the effects of air resistance. (2)
(c) A joulemeter measures the amount of energy transferred electrically to the motor as the motor lifts the load.
The joulemeter displays a reading of 11.0 J when the load has gained 3.2 J of energy in its gravitational store.
(i) Calculate the efficiency of the motor. (3)
efficiency = ……………………………………………………..
(ii) Justify why 7.8 J of energy must be dissipated into the thermal store of the surroundings as the load is lifted. (2)
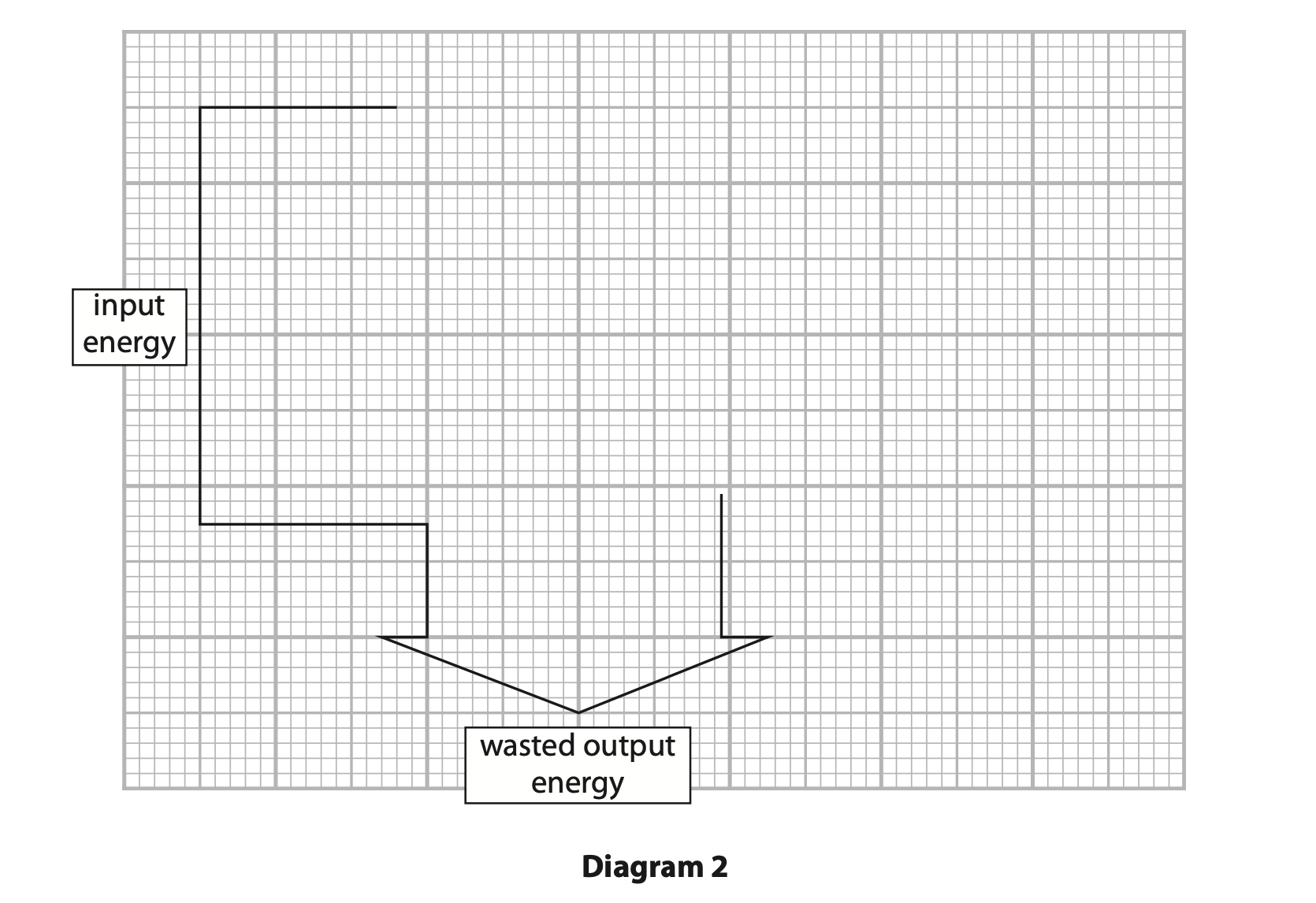
(iii) Diagram 2 is an incomplete Sankey diagram.
Complete the Sankey diagram to show the energy transferred by the motor. (3)
(Total for Question 3 = 15 marks)
June 2023 Paper 1PR Q10
10 A dam is a structure designed to hold water in a reservoir.
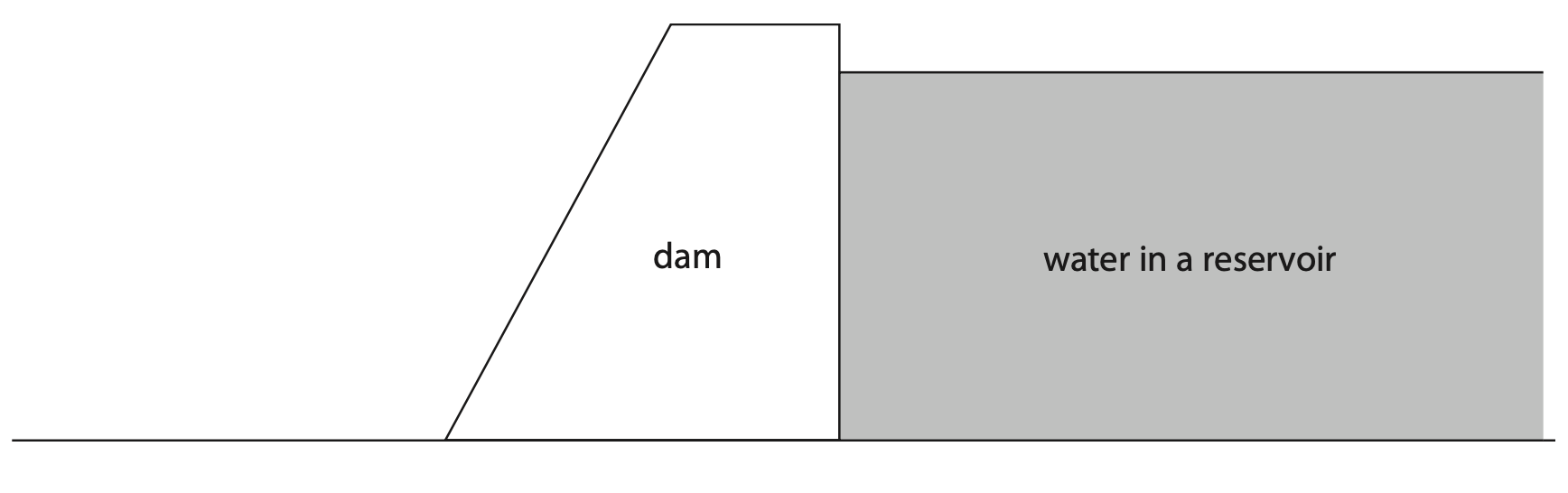
(a) The water in the reservoir has a depth of 35 m.
(i) State the formula linking pressure difference, height, density and g.(1)
(ii) Atmospheric pressure at the surface of the reservoir is 100 kPa. Calculate the total pressure at the bottom of the reservoir.
[for water, density = 1000 kg / m3] (3)
pressure = …………………………………………………….. kPa
(b) An underwater camera is used in the water reservoir.
The camera lens experiences a force of 430 N at a pressure of 260 kPa.
(i) State the formula linking pressure, force and area. (1)
(ii) Calculate the area of the camera lens.
Give a suitable unit. (4)
area = …………………………………………………….. unit ……………………………………………………..
(c) Sea water has a density of 1030 kg / m3.
Explain how the design of the dam would need to be changed to hold the same depth of sea water safely. (2)
(Total for Question 10 = 11 marks)
June 2023 Paper 2PR Q2
2 This question is about different methods of generating electricity.
(a) Natural gas can be burned to generate electricity.
Name the energy store that decreases when natural gas is burned. (1)
(b) Burning natural gas and the movement of water waves can both be used to generate electricity.
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of these two methods of generating electricity. (4)
(Total for Question 2 = 5 marks)
November 2023 Paper 1P Q5
5 A student uses this apparatus to investigate energy transfer by conduction in metals.
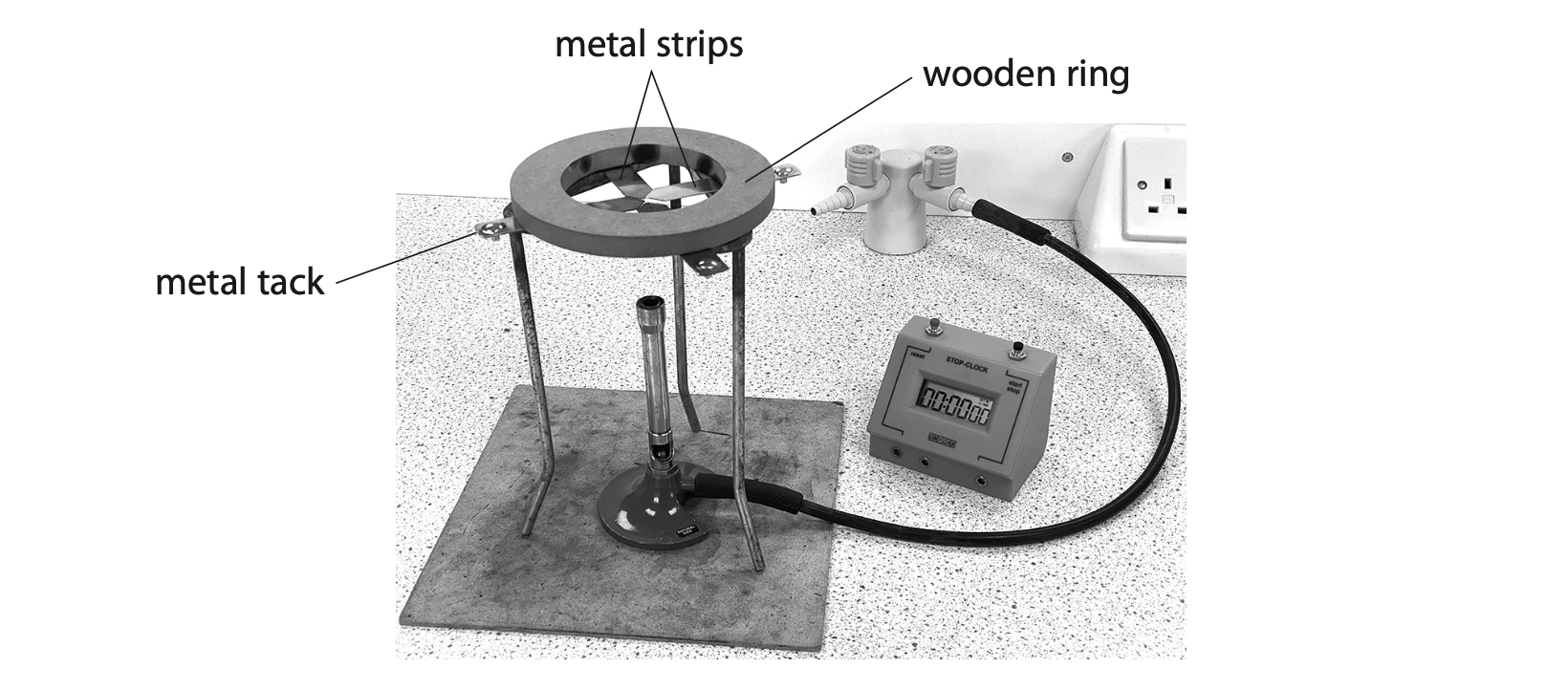
This is the student’s method.
- attach four strips, each made of a different metal, to a wooden ring
- use wax to attach a metal tack to the end of each metal strip
- place the strips above a Bunsen burner
- light the Bunsen burner and start a stopwatch at the same time
- when enough energy has been transferred to the wax, it melts, causing the metal tack to fall
- record the time taken for each tack to fall
(a) Explain how the wooden ring makes the apparatus safer for the student to use. (3)
(b) Describe how energy is transferred by conduction through the metal strips. (3)
(c) The bar chart shows the results of the student’s investigation.
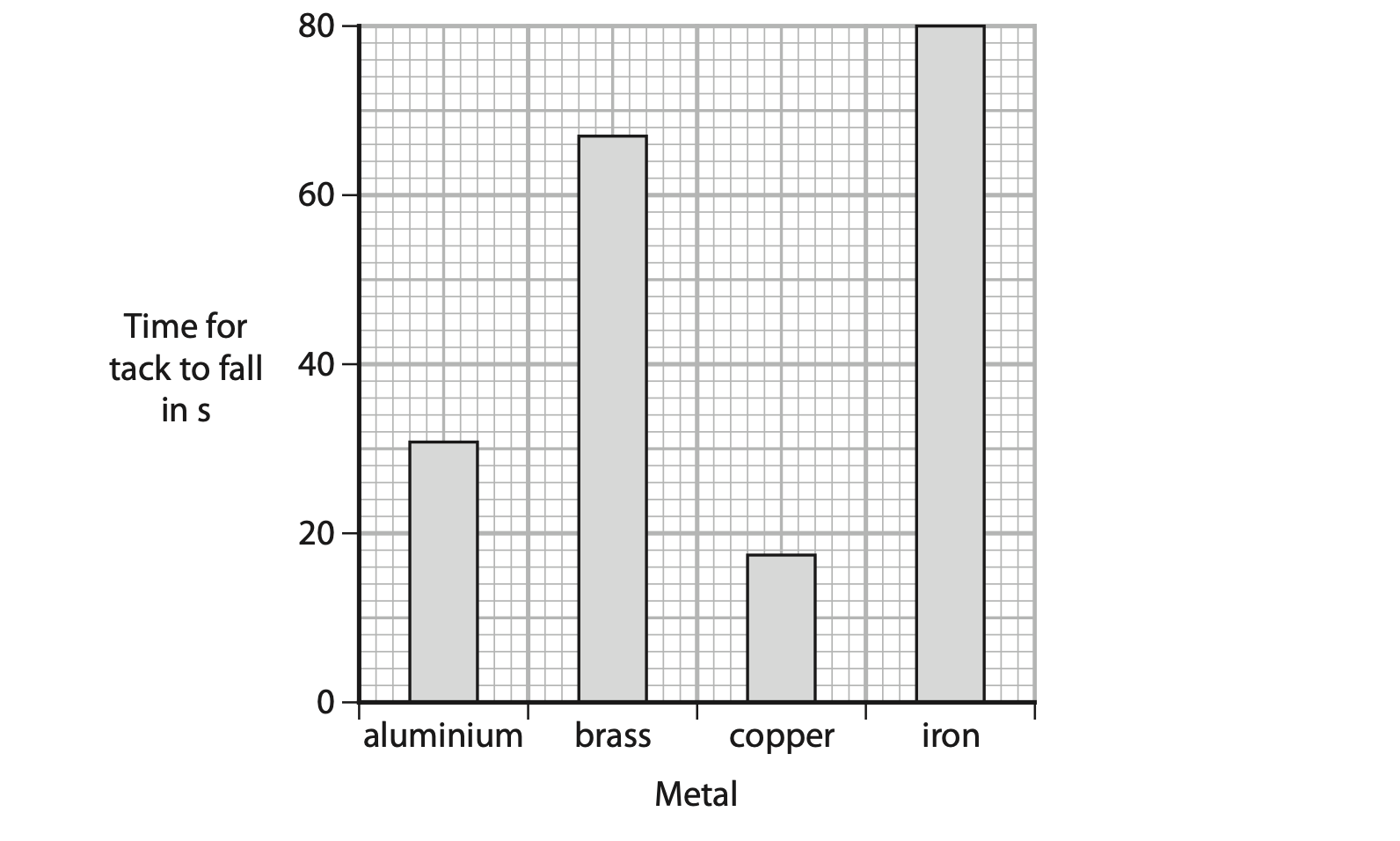
(i) Justify the use of a bar chart in this investigation. (1)
(ii) State how the student could improve the reliability of their results. (2)
(iii) The student concludes that iron is the best metal for transferring energy by conduction.
Evaluate the student’s conclusion. (2)
(Total for Question 5 = 11 marks)
November 2023 Paper 1P Q12
12. The photograph shows a toy called a marble run.

A student lifts a marble from the table to the top of the marble run at point A. They release the marble from point A and it rolls through pipes to reach the bottom of the marble run at point B.
The marble leaves the marble run at point B and rolls across the table.
As the marble rolls, energy is transferred due to the different forces acting on the marble.
(a) Describe the energy transfers from before the student lifts the marble to when the marble reaches point B of the marble run. (5)
(b) The student wants to measure how much energy the marble loses as it moves from point A to point B.
(i) The student needs to measure the speed of the marble as it leaves the marble run at point B.
Describe a method the student could use to measure this speed. (3)
(ii) The difference in height between point A and point B is 0.21 m.
The mass of the marble is 5.5 g.
The marble leaves the marble run at point B with a speed of 0.76 m/s.
Calculate the energy lost by the marble as it rolls from point A to point B. (5)
energy lost = …………………………………………………….. J
(Total for Question 12 = 13 marks)
Nov 2023 Paper 2P Q3
3 The diagram shows some apparatus that can be used to determine the specific heat capacity of water.
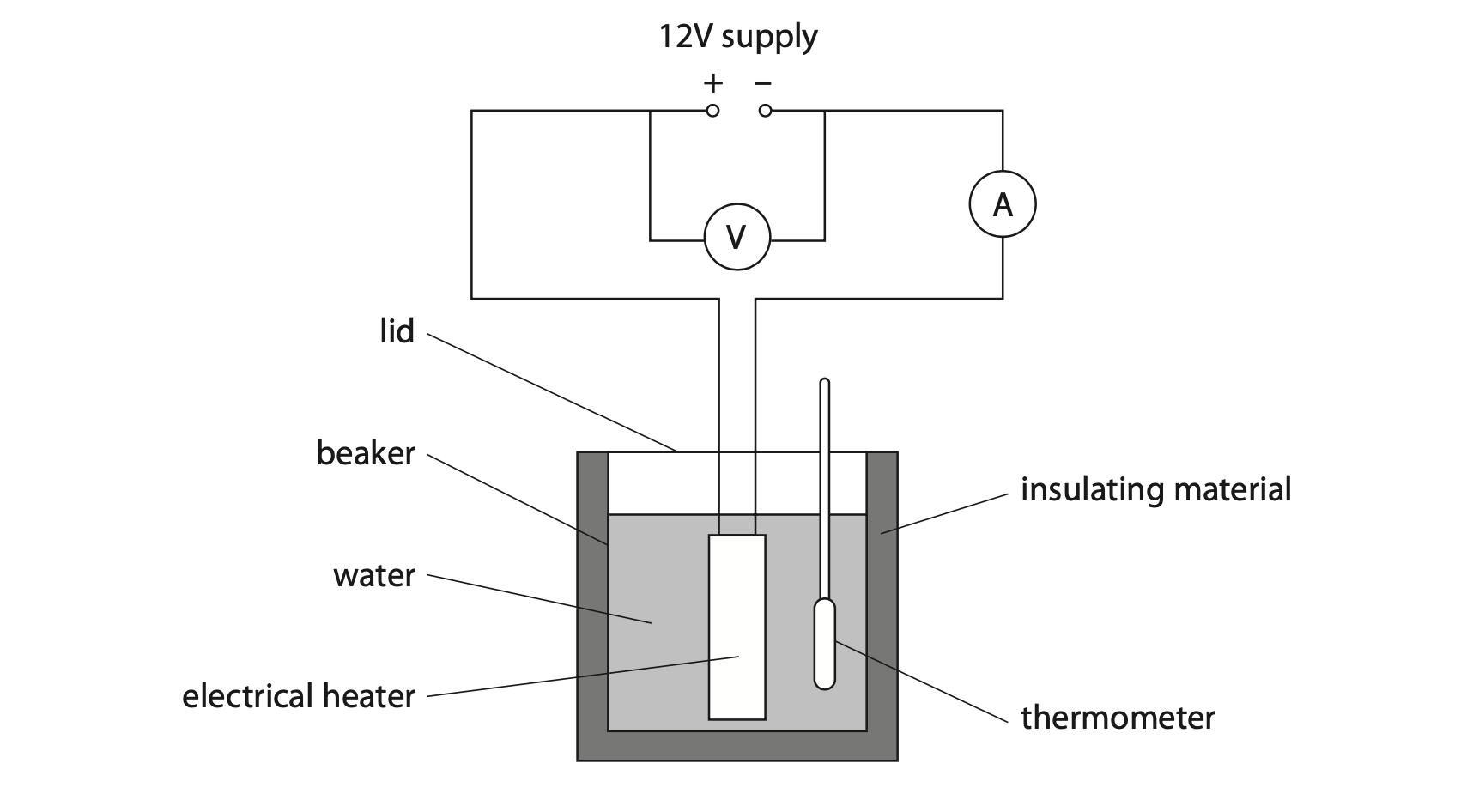
(a) Describe how a student could use this apparatus to determine the specific heat capacity of water.
Include details of any additional equipment needed in your answer. (6)
b) (i) The table shows the student’s results.
| energy transferred to the thermal store of the water in J | 54 000 |
| mass of water in kg | 0.56 |
| temperature change of water in °C | 22 |
Use the student’s results to calculate the specific heat capacity of water. (3)
specific heat capacity of water = …………………………………………………….. J/kg°C
(ii) Give two reasons why the energy from the heater is not all retained in the thermal store of the water. (2)
1
2
(Total for Question 3 = 11 marks)











