IGCSE Physics Past Years Exam Questions: Waves 2023-24
We analysed the International GCSE past papers and grouped the questions by topic. Here, you will find questions relating to the topic – Waves. Use these to familiarise, practice and prepare for your IGCSE Physics examination.
You can find earlier below:
- IGCSE Physics Past Year Questions on Waves from 2019 to 2020
- IGCSE Physics Past Year Questions on Waves from 2021 to 2022
What you need to know
Use the list below as a quick recap for what you need to know before attempting the past year exam questions under this topic. This is based on Edexcel International GCSE in Physics (4PH1) specification with first teaching Sept 2017 and first examination June 2019.
Paper 1 and 2: (3) Waves
Paper 1 covers all the topics except where it is marked “paper 2 only” while Paper 2 covers all topics.
A. UNITS
- degree (°), hertz (Hz), metre (m), metre/second (m/s) and second (s)
B. PROPERTIES OF WAVES
- explain differences between longitudinal and transverse waves.
- definitions of amplitude, wavefront, frequency, wavelength and period of a wave.
- waves transfer energy and information without transferring matter.
- the relationship between wave speed, wavelength and frequency. v=f×λ
- the relationship between frequency and time period. f=1/T
- use the relationships above in different contexts
- the Doppler effect: change in observed frequency and wavelength when its source is moving relative to observer
- that all waves are reflected and refracted
C. THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM
- that light is part of a continuous electromagnetic spectrum: radio, microwave, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, x-ray, gamma ray.
- that all these waves travel at the same speeds in free space
- the order of electromagnetic spectrum by wavelength and frequency (decreasing wavelengths, increasing frequency, colours of visible spectrum)
- explain the uses of electromagnetic radiations: radio waves (broadcasting, communications), microwaves (cooking, satellite transmissions), infrared (heaters, night vision), visible light (optical fibres, photography), ultraviolet (fluorescent lamps), x-ray (observe internal structure, medical), gamma rays (sterilising food, medical equipment)
- explain the detrimental effects of the electromagnetic waves: microwave (internal heating of body tissue), infrared (skin burns), ultraviolet (damage to surface cells and blindness), gamma ray (cancer, mutation). Describe protective measures.
D. LIGHT AND SOUND
- that light waves are transverse waves and can be reflected and angle of refracted
- use the law of reflection. (angle of incidence = angle of reflection)
- draw ray diagrams to show reflection and refraction
- investigate the refraction of light
- the relationship between refractive index and the angle of incidence and angle of refraction. n = sin i / sin r
- investigate the refractive index using glass block
- describe the role of total internal reflection in optical fibres and prisms
- explain the meaning of critical angle, c
- relationship between critical angle and refractive index. sin c = 1 / n
- sound waves are longitudinal and can be reflected and refracted
(paper 2 only)
- range of human hearing 20-20000Hz
- investigate the speed of sound in air
- how an oscilloscope and a microphone can display sound waves
- investigate the frequency of sound with an oscilloscope
- that pitch of sound relates to frequency of the source vibration
- that loudness relates to the amplitude of the source vibration
Jan 2023 Paper 1P Q6
6. This question is about optical fibres.
(a) Optical fibres use light waves for communication.
Which of these is a correct statement about waves? (1)
A waves transfer energy, information and matter
B waves do not transfer energy, information, or matter
C waves transfer energy without transferring information or matter
D waves transfer energy and information without transferring matter
(b) A ray of light passes from air into a glass optical fibre.
Diagram 1 shows the path of the ray of light after it has passed through the boundary between air and the optical fibre.
(i) Draw the path of the ray of light in air before it passed through the boundary. (1)
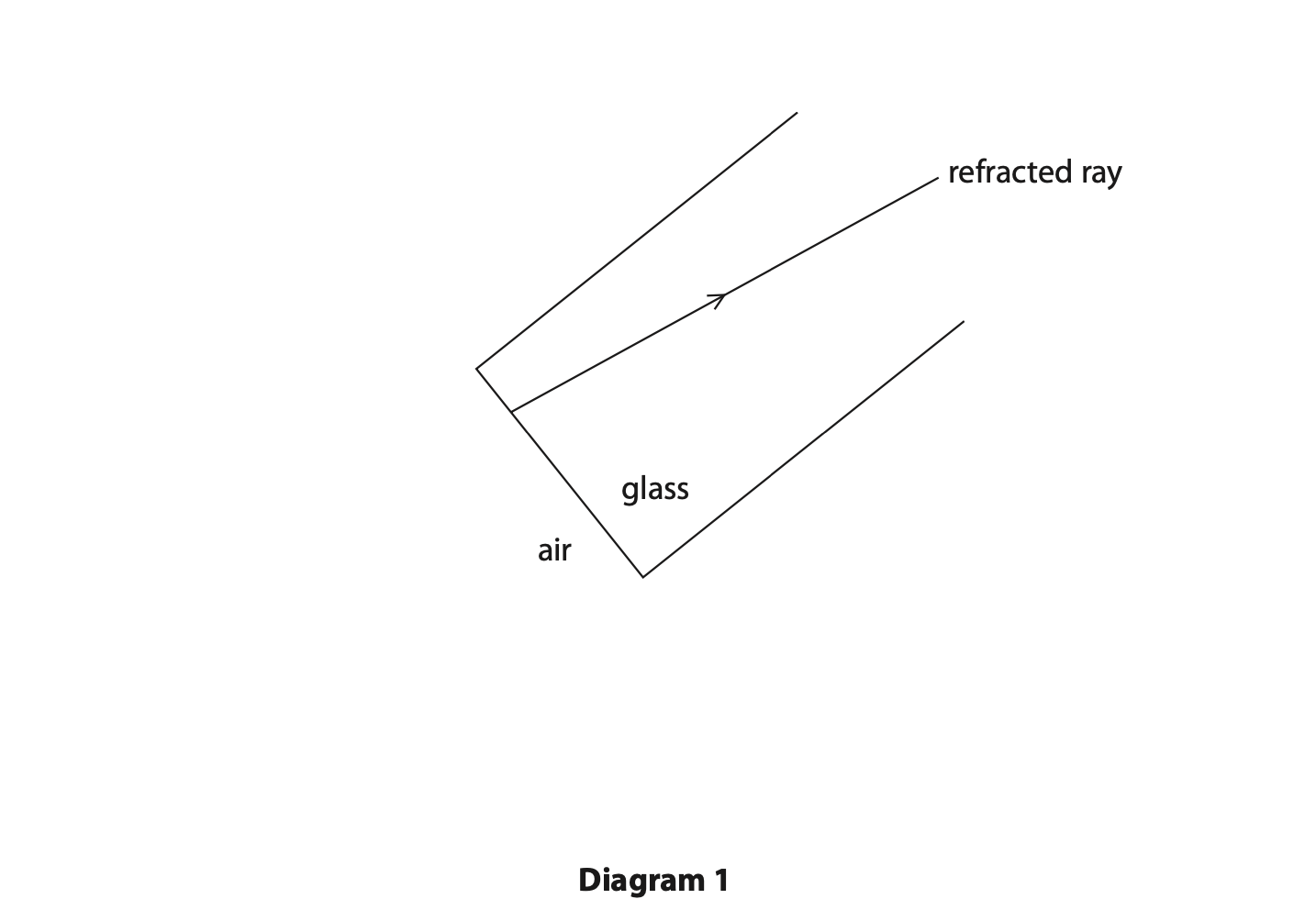
(ii) State the name of the wave behaviour responsible for the path of the ray of light as it passes from air into the optical fibre. (1)
(c) Diagram 2 shows the path of the ray of light as it travels through the optical fibre.
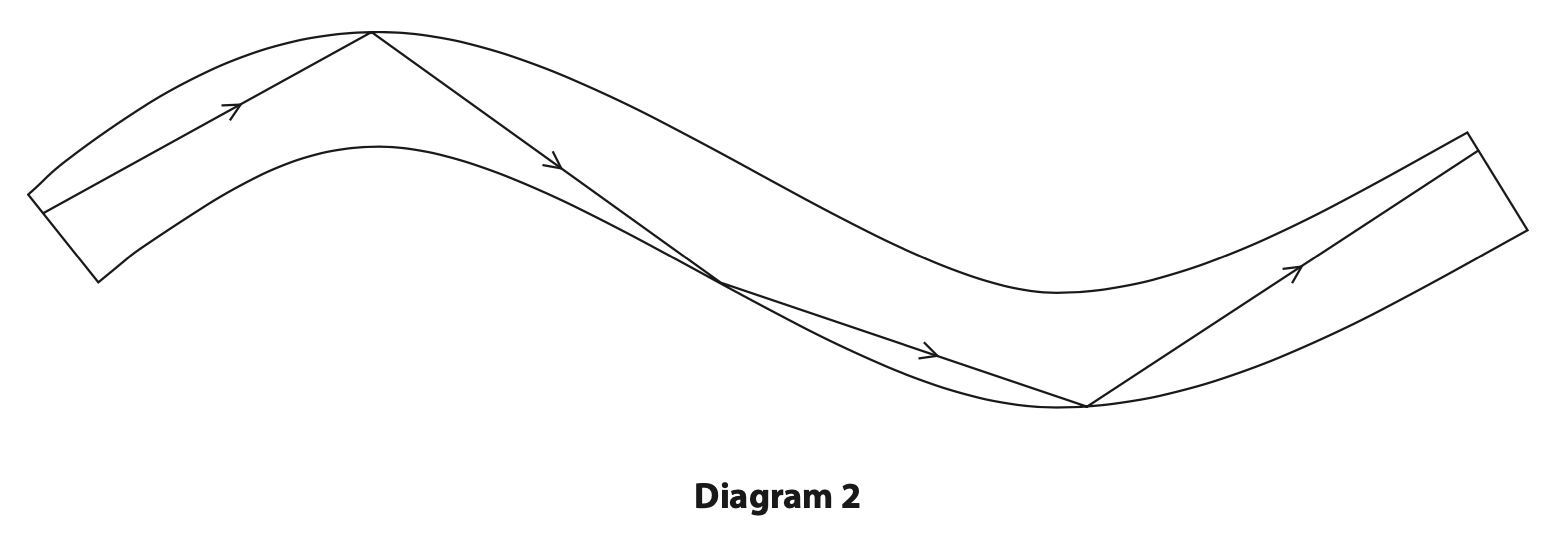
Explain the path of the ray of light as it travels through the optical fibre. (3)
(Total for Question 6 = 6 marks)
Jan 2023 Paper 1P Q9
9 This question is about waves.
(a) The diagram represents a wave.
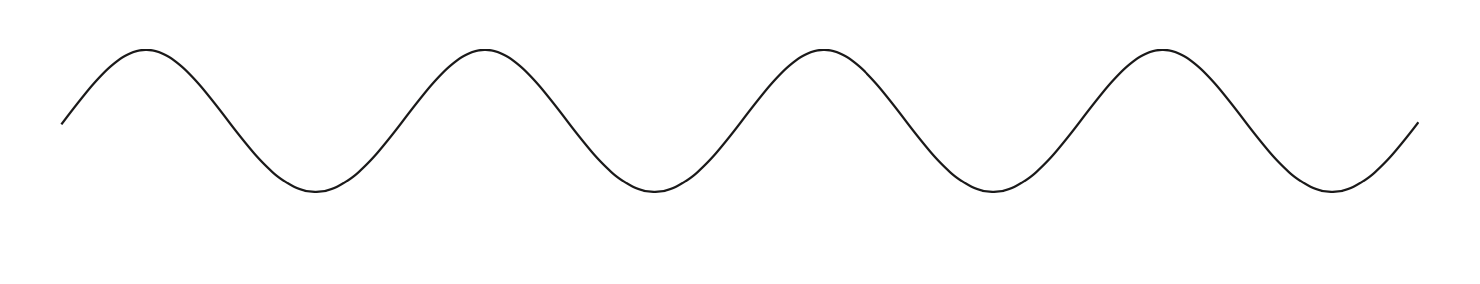
(i) Determine the amplitude of the wave by measuring it with a ruler.(1)
amplitude = …………………………………………………….. cm
(ii) Determine the wavelength of the wave by measuring it with a ruler. (1)
wavelength = …………………………………………………….. cm
(b) Microwaves are part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
(i) Name the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that has a lower frequency than microwaves. (1)
(ii) Microwaves travel at a speed of 3.0 × 108 m / s in air.
A microwave has a wavelength of 2.7 cm.
Calculate the frequency of this microwave.
[wave speed = frequency × wavelength] (3)
frequency = …………………………………………………….. Hz
(c) A student uses a microwave source and a receiver to investigate microwaves.
Photograph 1 shows how the student sets up their apparatus.
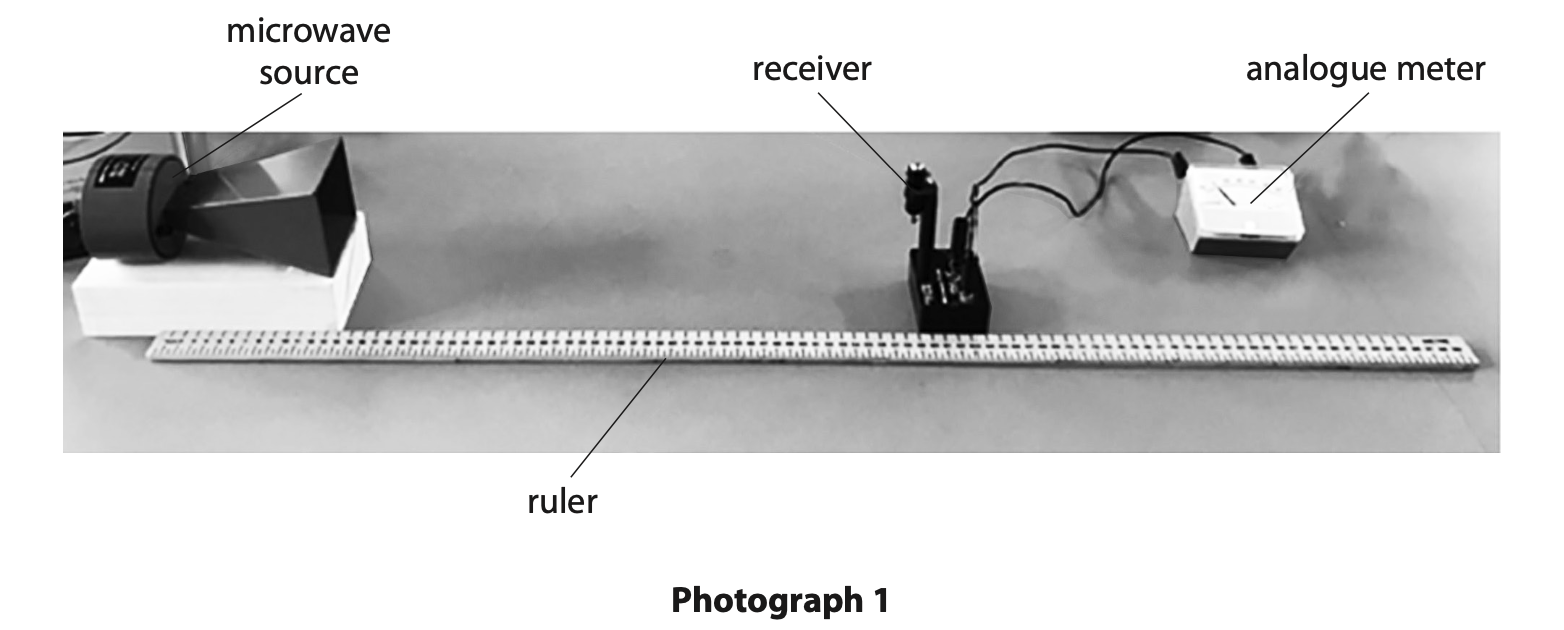
The meter shows the strength of the microwaves detected by the receiver.
The strength of the microwaves is measured in arbitrary units.
The student varies the distance between the microwave source and the receiver, and records the meter readings.
(i) Photograph 2 shows the analogue meter for one of the readings.
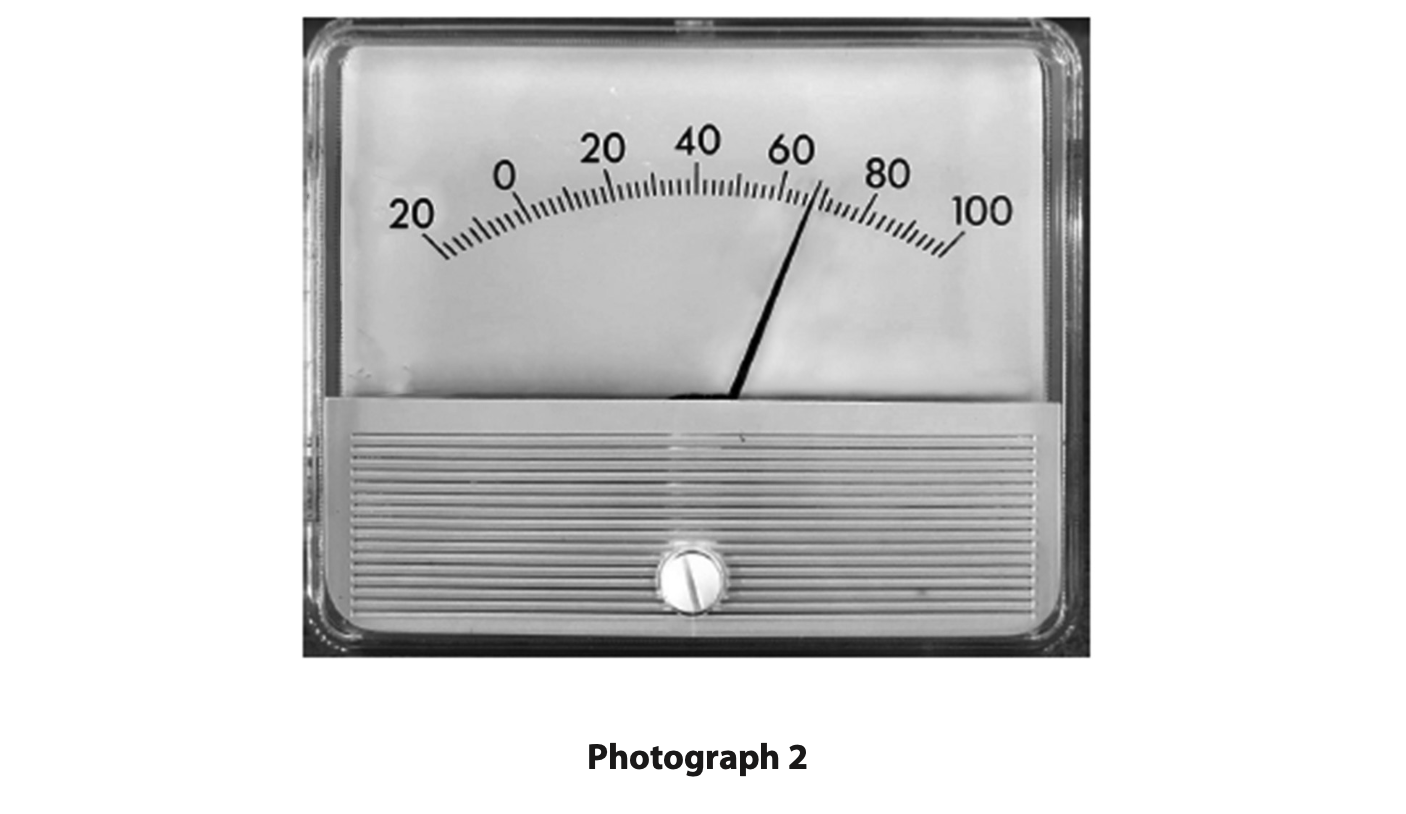
Give the reading on the analogue meter. (1)
reading = …………………………………………………….. arbitrary units
(ii) The graph shows the results of the student’s investigation.
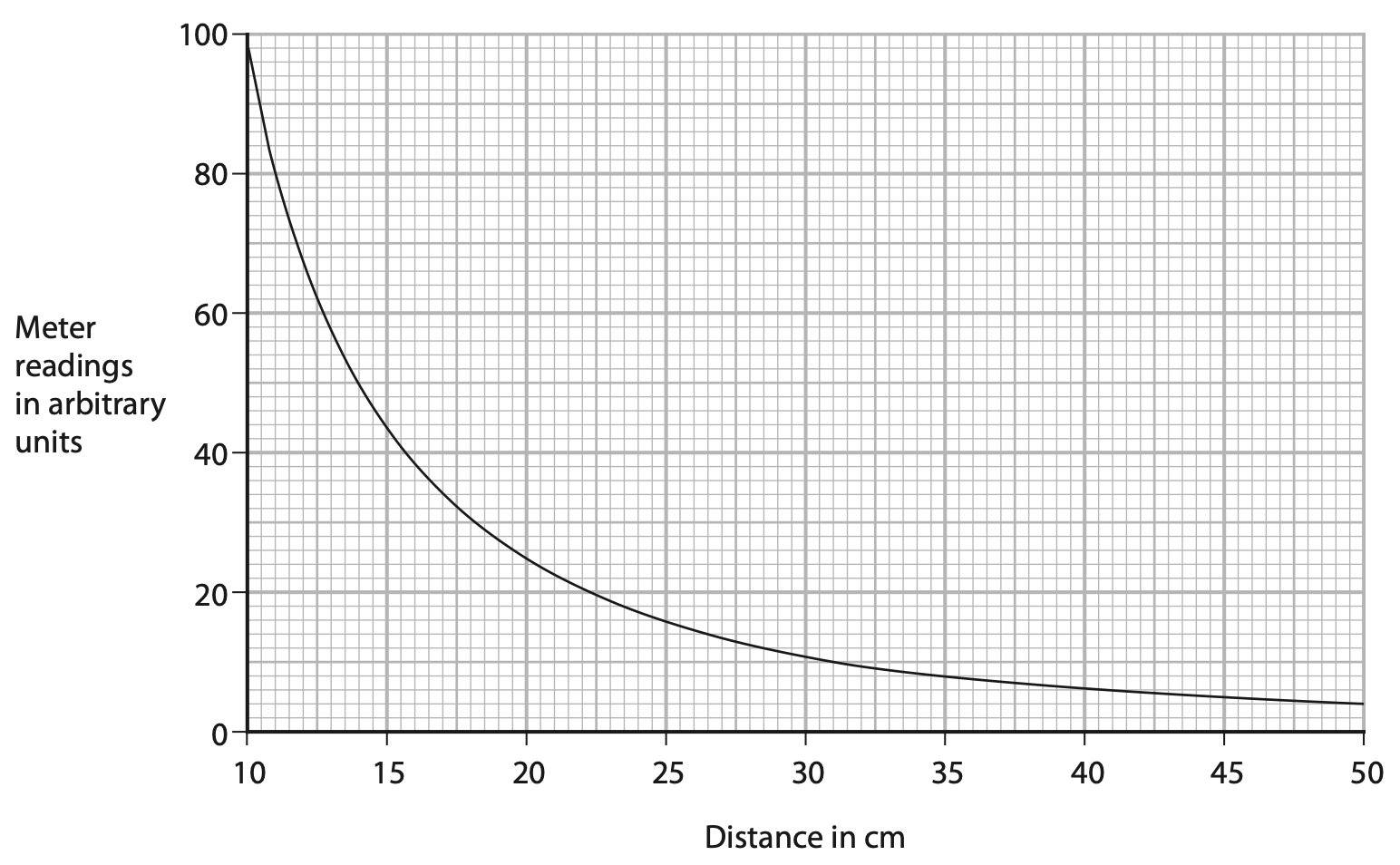
The student concludes that the meter reading is inversely proportional to the distance between the microwave source and the receiver.
To be inversely proportional
meter reading × distance = constant
Comment on the student’s conclusion.
You should use data from the graph in your answer. (4)
(Total for Question 9 = 11 marks)
January 2023 1PR Q1
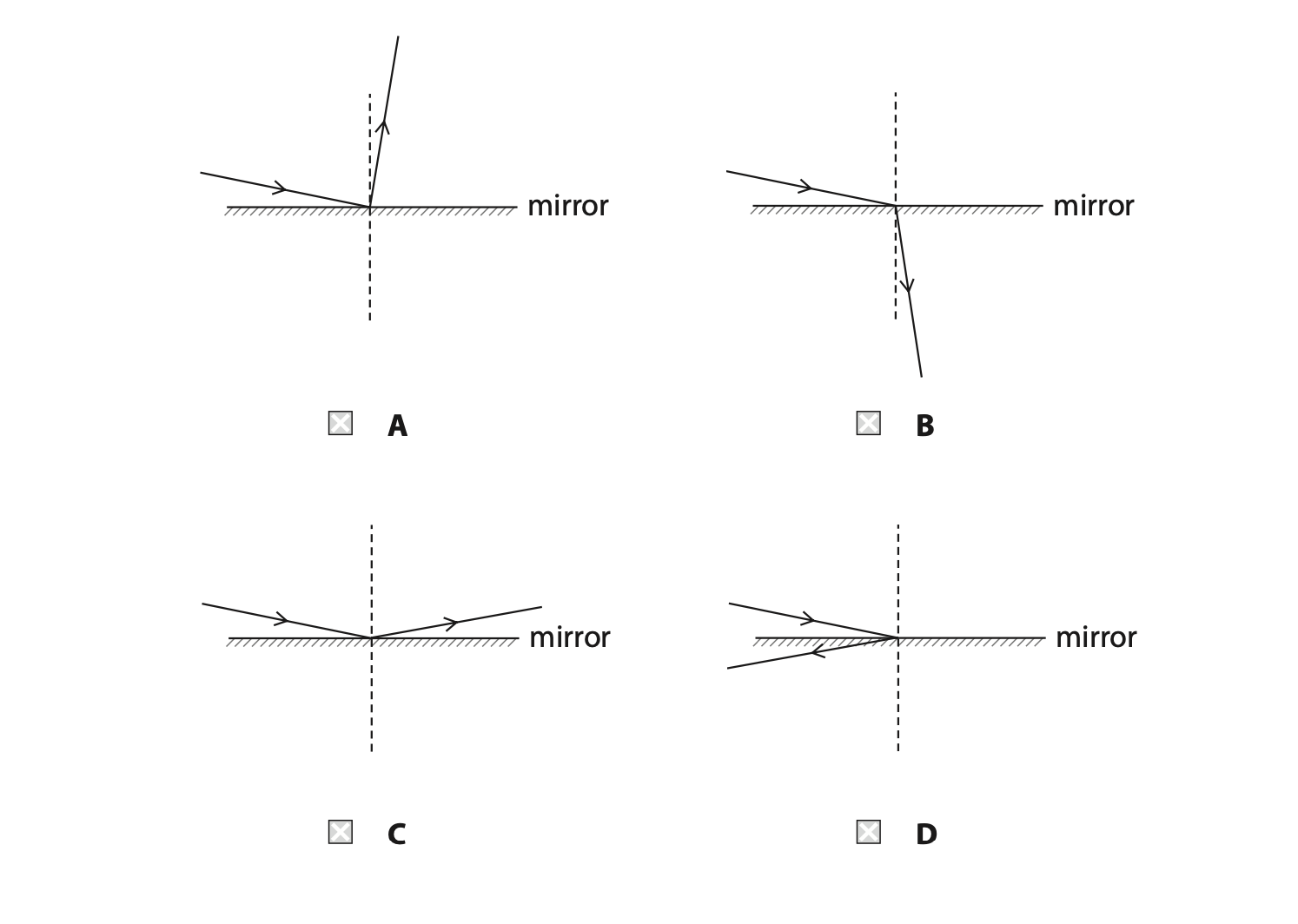
1. This is a question about reflection.
(a) Which diagram shows a light ray correctly reflected from a mirror? (1)
(b) Name the equipment needed to measure the angle of incidence on a ray diagram. (1)
(c) Light from a laser on the Earth reflects off special mirrors on the Moon.
The graph shows the data from a light sensor attached to the laser.
The first peak shows when the light leaves the laser and the second peak shows when the light has returned from the Moon.
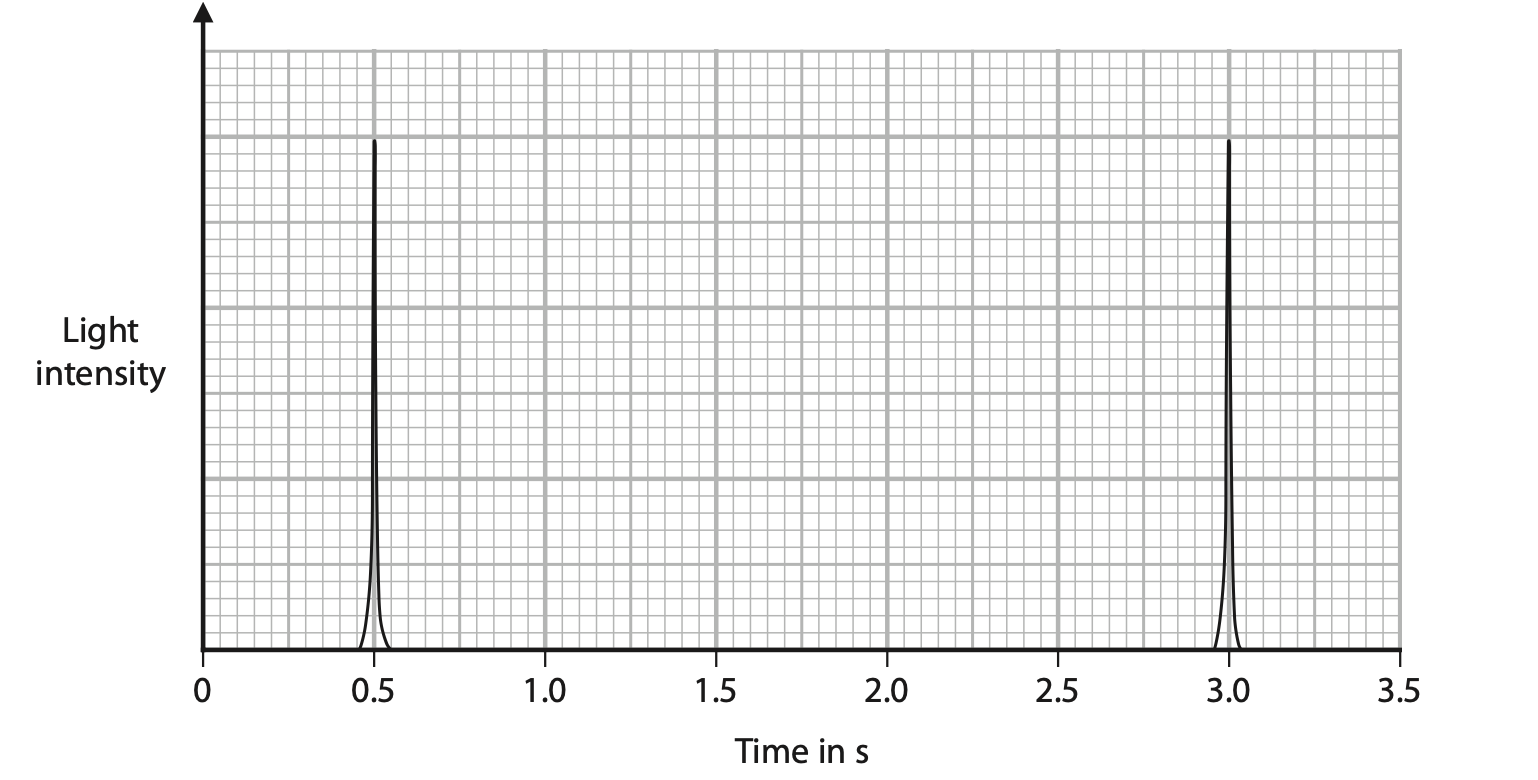
(i) Determine the time taken for the light to travel from the Earth to the Moon and back again. (2)
time taken = …………………………………………………….. s
(ii) The speed of light is 3.0 × 105 km/s.
Calculate the total distance travelled by the light from the laser. (2)
[average speed = distance moved ÷ time taken]
total distance = …………………………………………………….. km
(iii) Calculate the distance from the Earth to the Moon. (1)
distance = …………………………………………………….. km
(Total for Question 1 = 7 marks)
January 2023 Paper 1PR
7. The diagram shows the path of a ray of light.
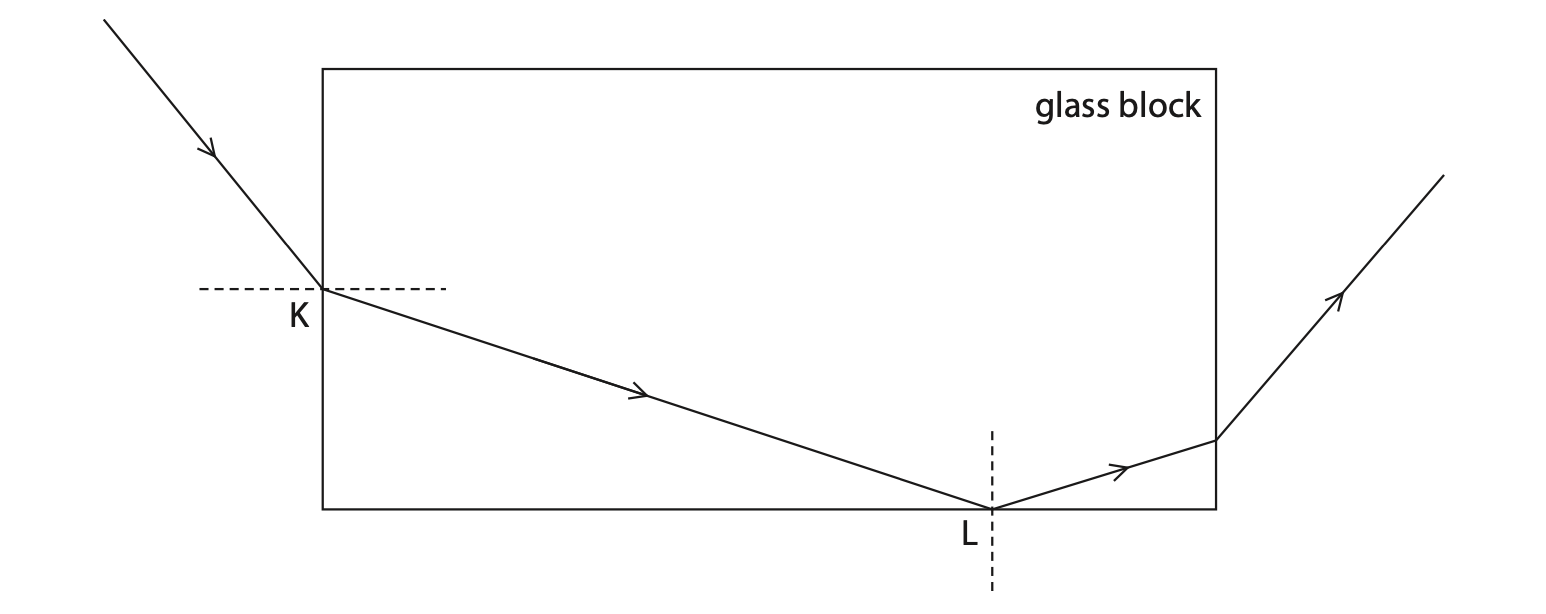
(a) (i) Measure the angle of incidence for the ray at point K. Which of these is the angle of incidence? (1)
A 43°
B 47°
C 51°
D 55°
(ii) State the formula linking refractive index, angle of incidence and angle of refraction. (1)
(iii) The block has a refractive index of 1.52
Use the formula to show that the angle of refraction is about 30° for the ray at point K. (3)
(b) (i) The refractive index of the block is 1.52
Calculate the critical angle of the block. (3)
(ii) State what happens to the ray at point L. (1)
(Total for Question 7 = 9 marks)
January 2023 Paper 2P Q7
7 A student uses this method to investigate the speed of sound in air.
- set up an oscilloscope to detect and display a sound wave
- use a computer and a speaker to produce a sound of known wavelength
- use the oscilloscope to determine the frequency of the sound wave
- use a formula to calculate the speed of sound
(a) Give the name of the equipment that should be connected to the oscilloscope to detect the sound wave.(1)
(b) The diagram shows the oscilloscope screen and the oscilloscope settings.

(i) Determine the frequency of the sound wave. (4)
frequency = …………………………………………………….. Hz
(ii) The wavelength of the sound wave is 27 cm.
Calculate the speed of sound. (3)
speed of sound = …………………………………………………….. m/s
(iii) Describe how the oscilloscope could be adjusted to show fewer wave cycles on the screen. (2)
(Total for Question 7 = 10 marks)
January 2023 Paper 2PR Q2
2. This is a question about electromagnetic waves.
(a) State which colour in the visible spectrum has the shortest wavelength. (1)
(b) Explain a hazard of ultraviolet radiation to the human body. (2)
(c) (i) State the formula linking speed, wavelength and frequency of a wave. (1)
(ii) Calculate the frequency of radio waves with a wavelength of 15 m. (2)
[speed of light = 300 000 000 m/s]
frequency = …………………………………………………….. Hz
(Total for Question 2 = 6 marks)
June 23 Paper 1P Q4
4 Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) uses radio waves to detect changes in material underground.
(a) (i) State the formula linking the speed, frequency and wavelength of a wave. (1)
(ii) GPR radio waves have a frequency of 170 MHz.
The speed of radio waves is 3.0 × 108 m / s.
Calculate the wavelength of the waves. (3)
wavelength = …………………………………………………….. m
(b) (i) A radio wave passes through the ground and refracts at the boundary between soil and rock.
The diagram shows three wavefronts of the wave before and after refraction.
The wave is also reflected at the boundary between the soil and the rock.
Complete the diagram to show three wavefronts after the wave has been reflected at the boundary. (3)
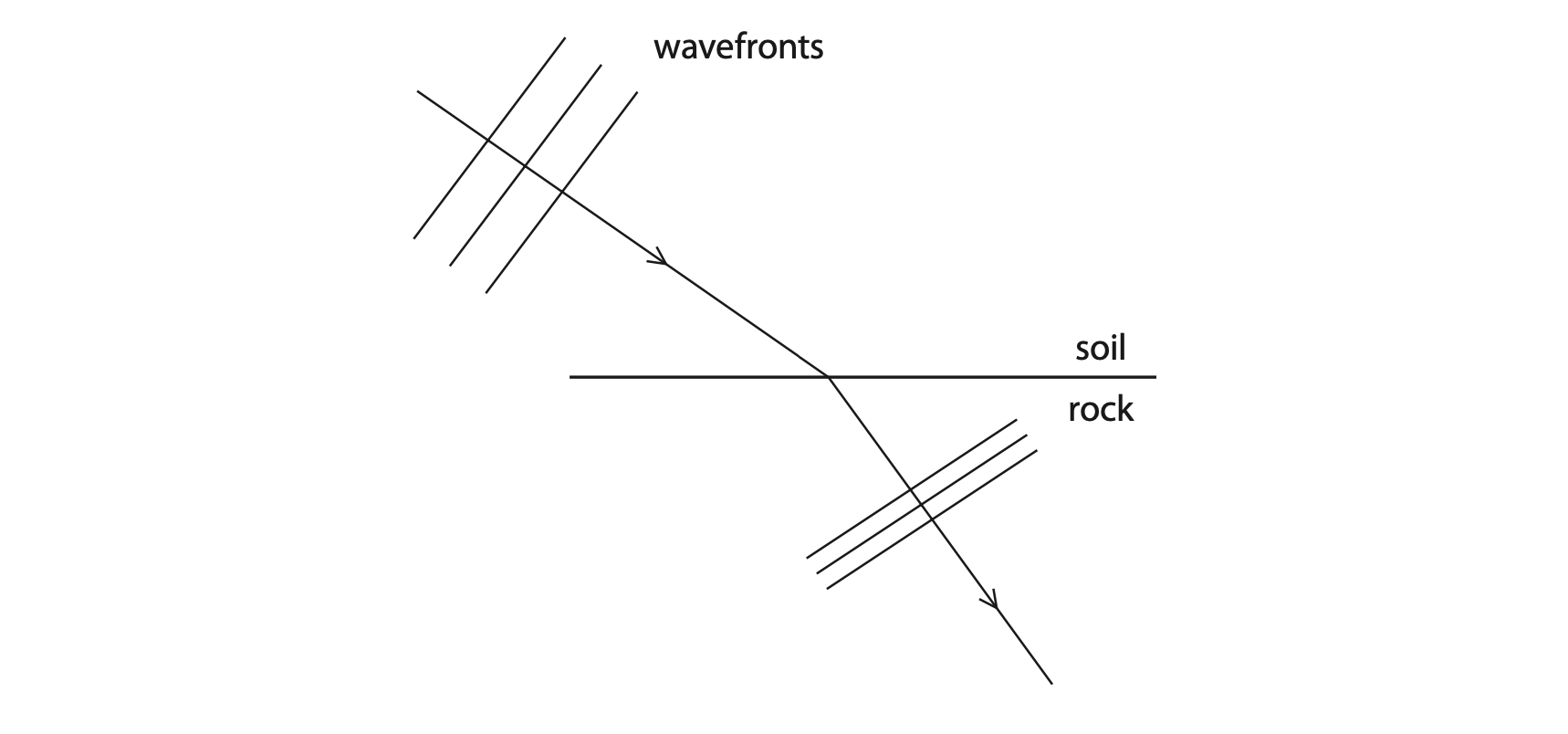
(ii) Explain why the radio waves passing through the rock have a smaller wavelength than the radio waves passing through the soil. (3)
(Total for Question 4 = 10 marks)
Jun 2023 Paper 1P Q6
6 The photograph shows an x-ray image of a person’s knee. The person has had part of their knee replaced.
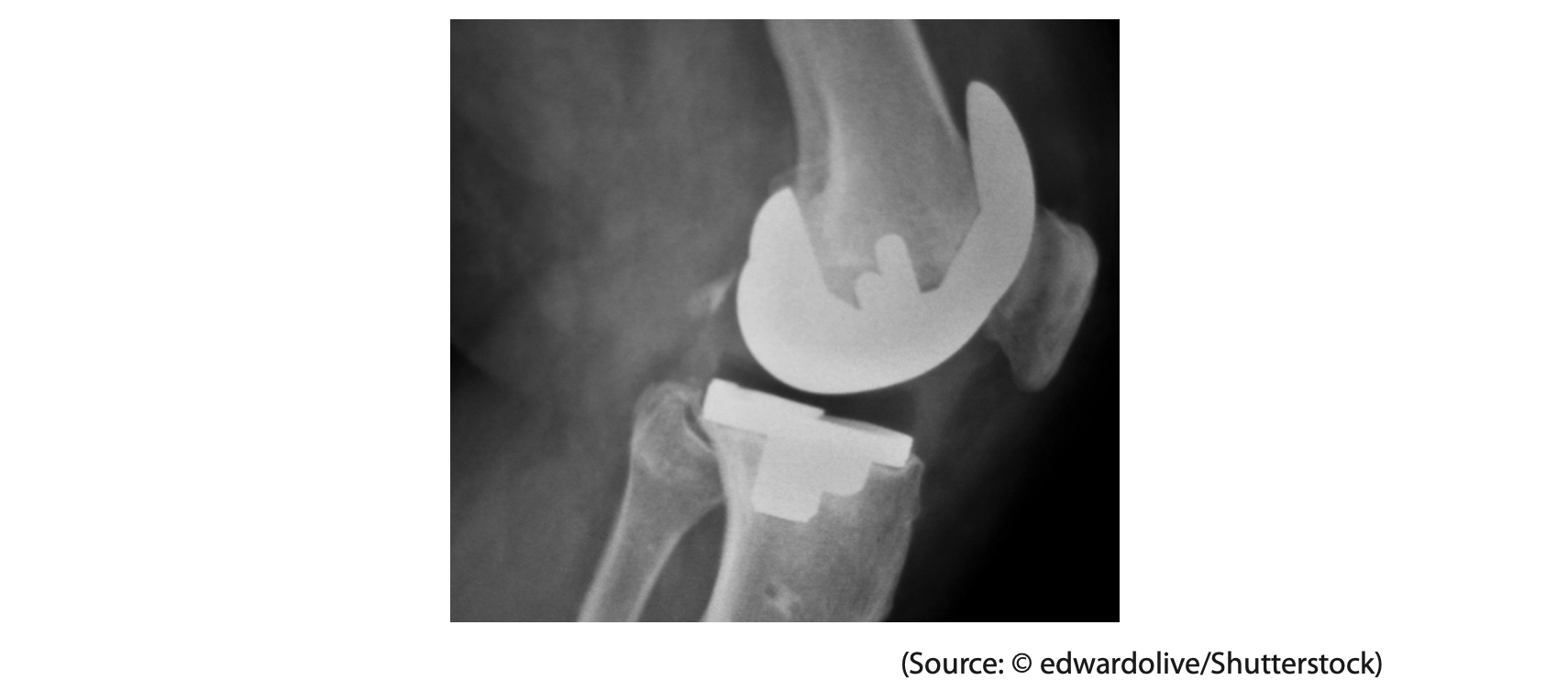
(a) X-rays are part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
All electromagnetic waves are transverse waves and transfer energy.
(i) State another property that all electromagnetic waves have in common. (1)
(ii) State a harmful effect of excessive exposure to x-rays. (1)
(iii) Describe the difference between transverse waves and longitudinal waves.
You may draw a diagram to help your answer. (3)
(b) The diagram shows a part of the knee called the patella. The patella has been removed from a person’s knee.
The patella is a small, irregularly shaped bone that is denser than water.
Describe how to find the mass and the volume of the patella bone. (4)
(c) A scientist finds the volume and mass of a patella.
The mass of the patella is 17 g.
The volume of the patella is 13 cm3.
Calculate the density of the patella.
Give your answer to 2 significant figures. (4)
density = …………………………………………………….. g/cm3
(Total for Question 6 = 13 marks)
June 2023 Paper 1PR Q1
1 This question is about the electromagnetic spectrum.
(a) The table gives some statements about the electromagnetic spectrum.
Place three ticks (✓) in the table to show which statements are correct. (3)
| Statement | Correct |
| all electromagnetic waves are longitudinal | |
| all electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed in free space | |
| radio waves have the longest wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum | |
| x-rays have the highest frequency in the electromagnetic spectrum | |
| all electromagnetic waves transfer energy | |
| all electromagnetic waves can cause cancer |
(b) Electromagnetic waves can be useful, but can also be harmful. (i) Give one use and one harmful effect of microwaves. (2)
use
harmful effect
(ii) Give one use and one harmful effect of gamma rays. (2)
use
harmful effect
(Total for Question 1 = 7 marks)
June 23 Paper 1PR Q5
5 A car is travelling in a straight line along a road. The car passes a person standing at the side of the road.
Before passing the person, the driver of the car presses the car’s horn. The horn makes a loud sound of constant frequency.
The horn continues to make a sound until after the car has passed the person.
Discuss the differences in the frequencies of the sound heard by
- the driver of the car
- the person at the side of the road
(Total for Question 5 = 6 marks)
June 23 Paper 2P Q7
7 (a) A glass prism can be used to refract light.
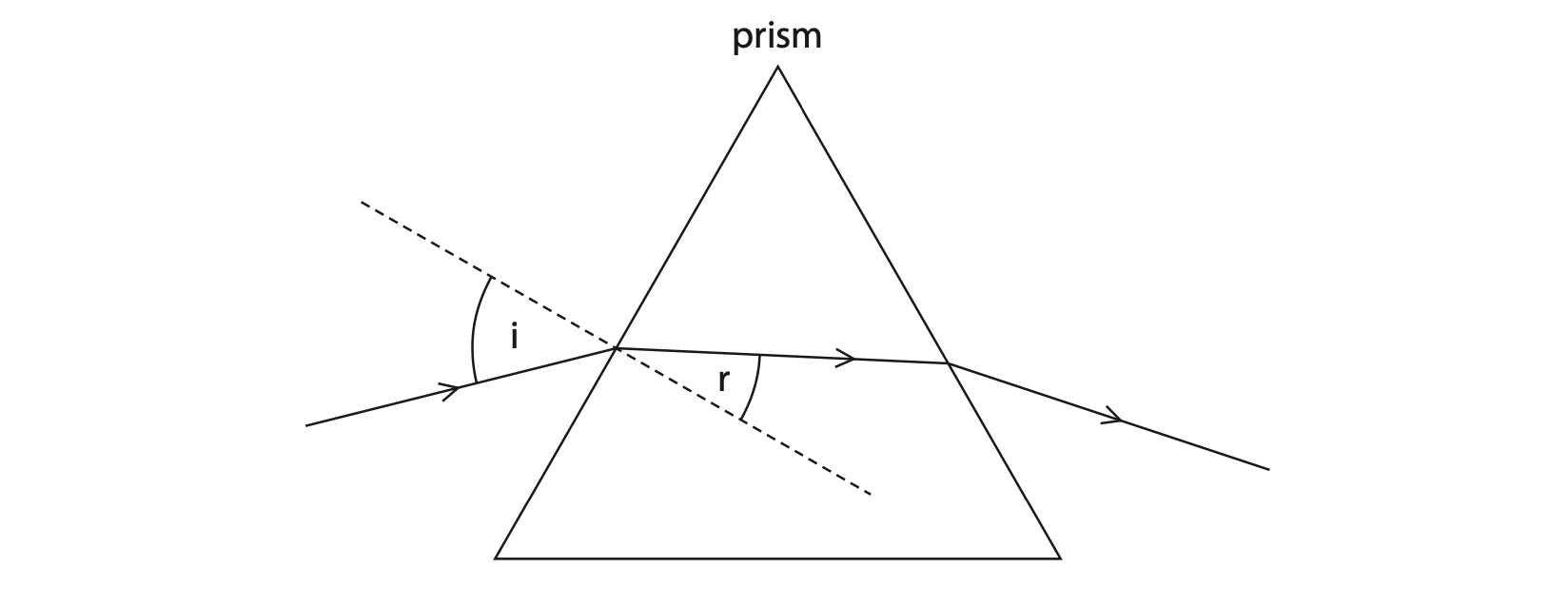
(i) State the name of the piece of equipment used to measure angles. (1)
(ii) Measure the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction for the light entering the prism. (2)
angle of incidence = …………………………………………………….. degrees
angle of refraction = …………………………………………………….. degrees
(iii) State the formula linking refractive index, angle of incidence and angle of refraction. (1)
(iv) Calculate the refractive index of the glass. (2)
refractive index = ……………………………………………………..
(b) Two galaxies, A and B, emit red light with a reference wavelength of 630 nm.
An astronomer measures the wavelength of red light from galaxy A when the light arrives at the Earth.
The astronomer’s value for the wavelength is 645 nm.
(i) Calculate the difference between the astronomer’s value for the wavelength and the reference wavelength of red light. (1)
difference in wavelength = …………………………………………………….. nm
(ii) The change in wavelength happens because galaxy A is moving away from the Earth.
Calculate the speed of galaxy A. (3)
[speed of light = 3.0 × 108 m/s]
speed = …………………………………………………….. m/s
(iii) Light from galaxy B has twice the redshift as light from galaxy A.
Galaxy B is twice as far away from Earth as galaxy A.
Explain how these observations support the Big Bang theory of the origin of the Universe. (2)
(Total for Question 7 = 12 marks)
June 2023 Paper 2PR Q7
7 This question is about sound waves.
(a) The table gives the frequencies of some different sound waves.
Place ticks (✓) in the table to show which sound waves can be heard by humans. (2)
| Sound wave | Frequency in Hz | Can be heard by humans |
| A | 10 | |
| B | 30 | |
| C | 500 | |
| D | 2000 | |
| E | 10 000 | |
| F | 25 000 |
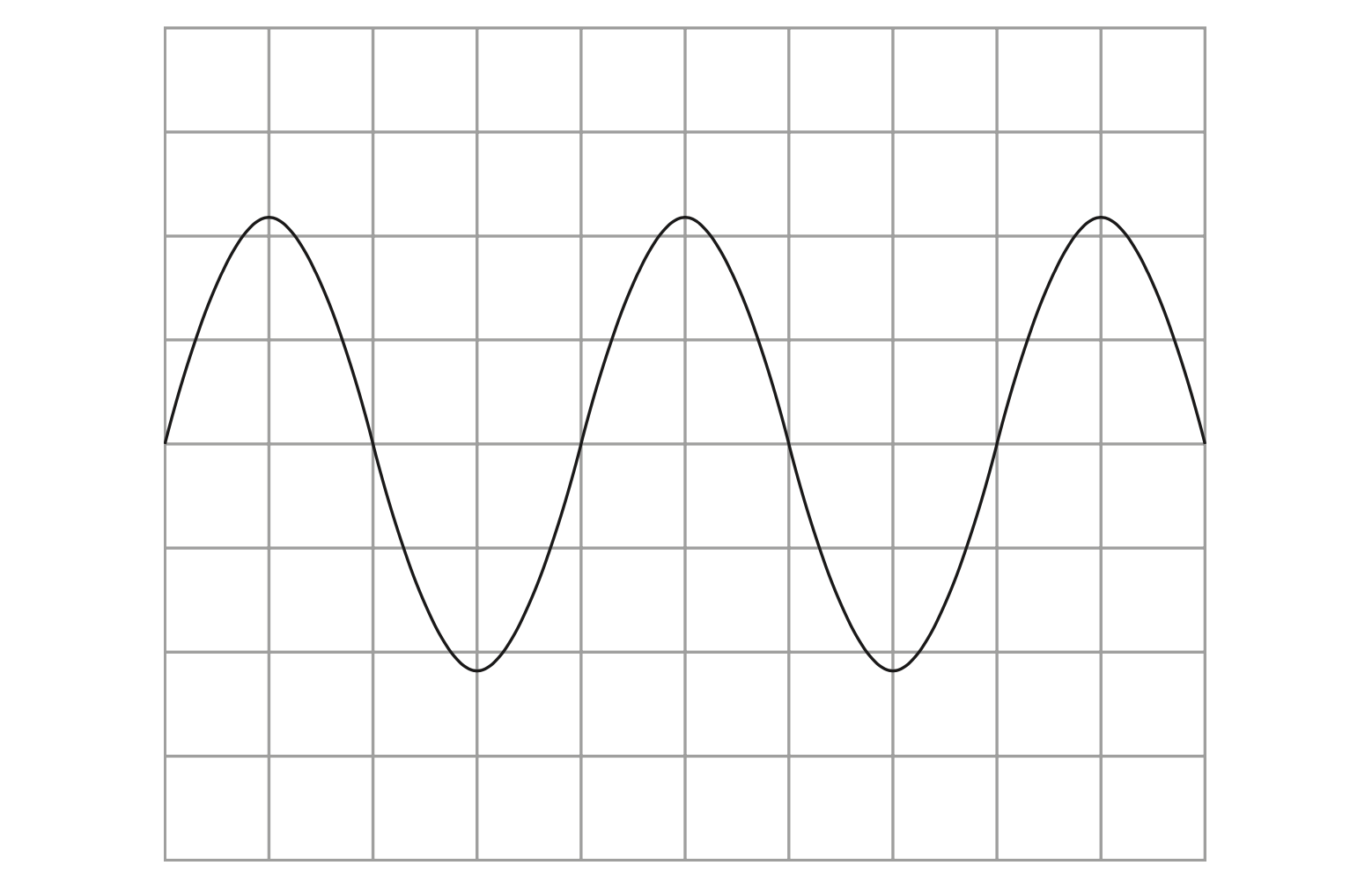
(b) The diagram shows the screen of an oscilloscope when a sound wave is detected.
Add to the diagram by drawing the trace of another sound wave that has a lower pitch and is quieter than the sound wave shown. (2)
(c) The speed of sound in air varies with temperature.
A student finds a formula in a textbook that links the speed of sound waves in air to the temperature of the air, measured in kelvin.
speed of sound in air = (0.606 × temperature in kelvin) + 166
(i) Calculate the speed of sound when the air temperature is 46 °C. (2)
speed of sound = …………………………………………………….. m/s
(ii) Calculate the wavelength of a sound wave with a frequency of 15 000 Hz when the air temperature is 46 °C. (3)
wavelength = …………………………………………………….. m
(Total for Question 7 = 9 marks)
Nov 2023 Paper 1P Q3
3 This question is about microwave ovens and microwaves. (a) A microwave oven cooks some food.
Diagram 1 represents a microwave emitted by the microwave oven.
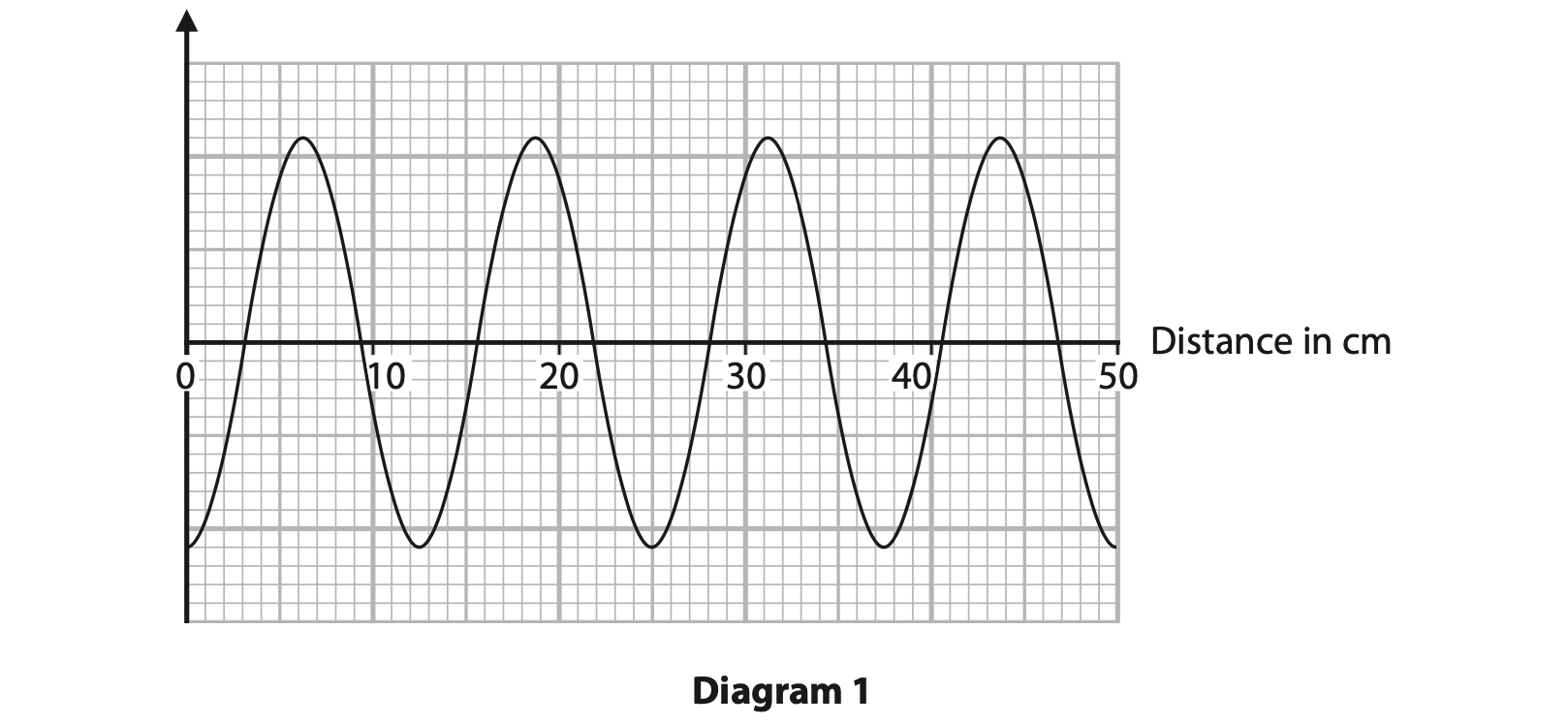
(i) Determine the wavelength of the microwave. (2)
wavelength = …………………………………………………….. cm
(ii) The microwave has a frequency of 2.35 GHz.
Show that the speed of the microwave is about 3 × 108 m/s. (3)
(b) Diagram 2 shows a damaged microwave oven with a hole in the door.
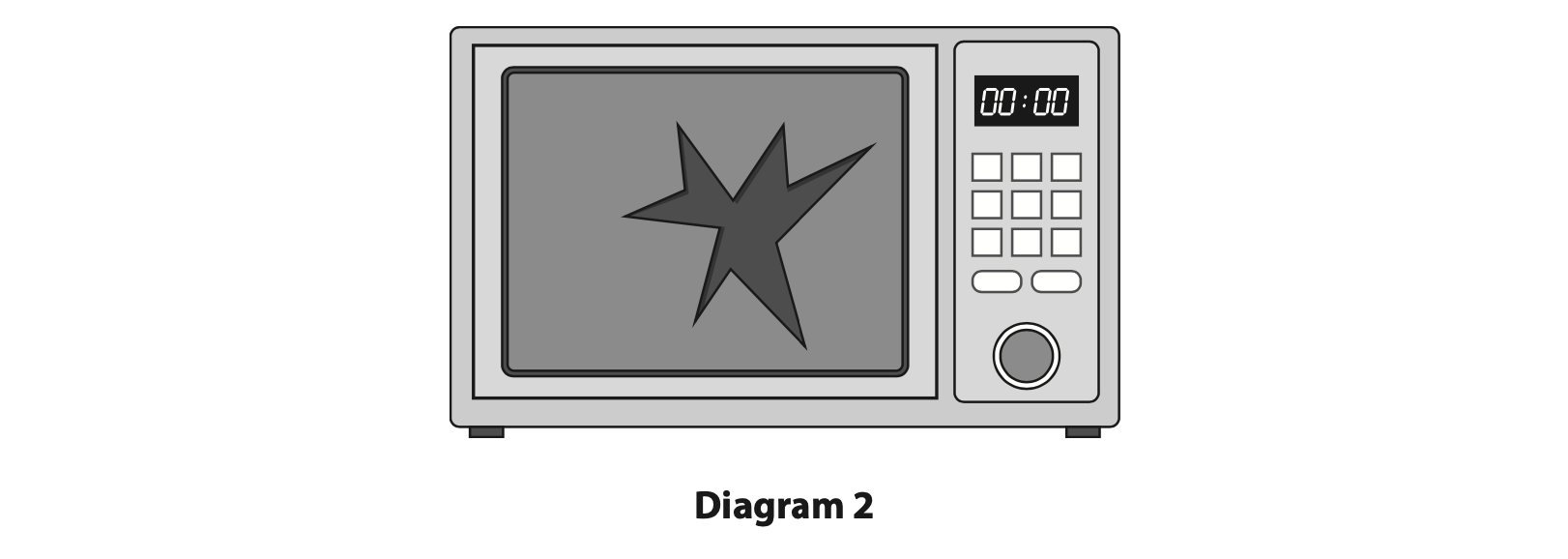
This microwave oven should not be used as it is very dangerous. State a harmful effect from the microwaves if this oven is used. (1)
(Total for Question 3 = 6 marks)
November 2023 Paper 2P Q7
7 The diagram shows the screen of an oscilloscope when a sound wave is detected, and the oscilloscope settings.
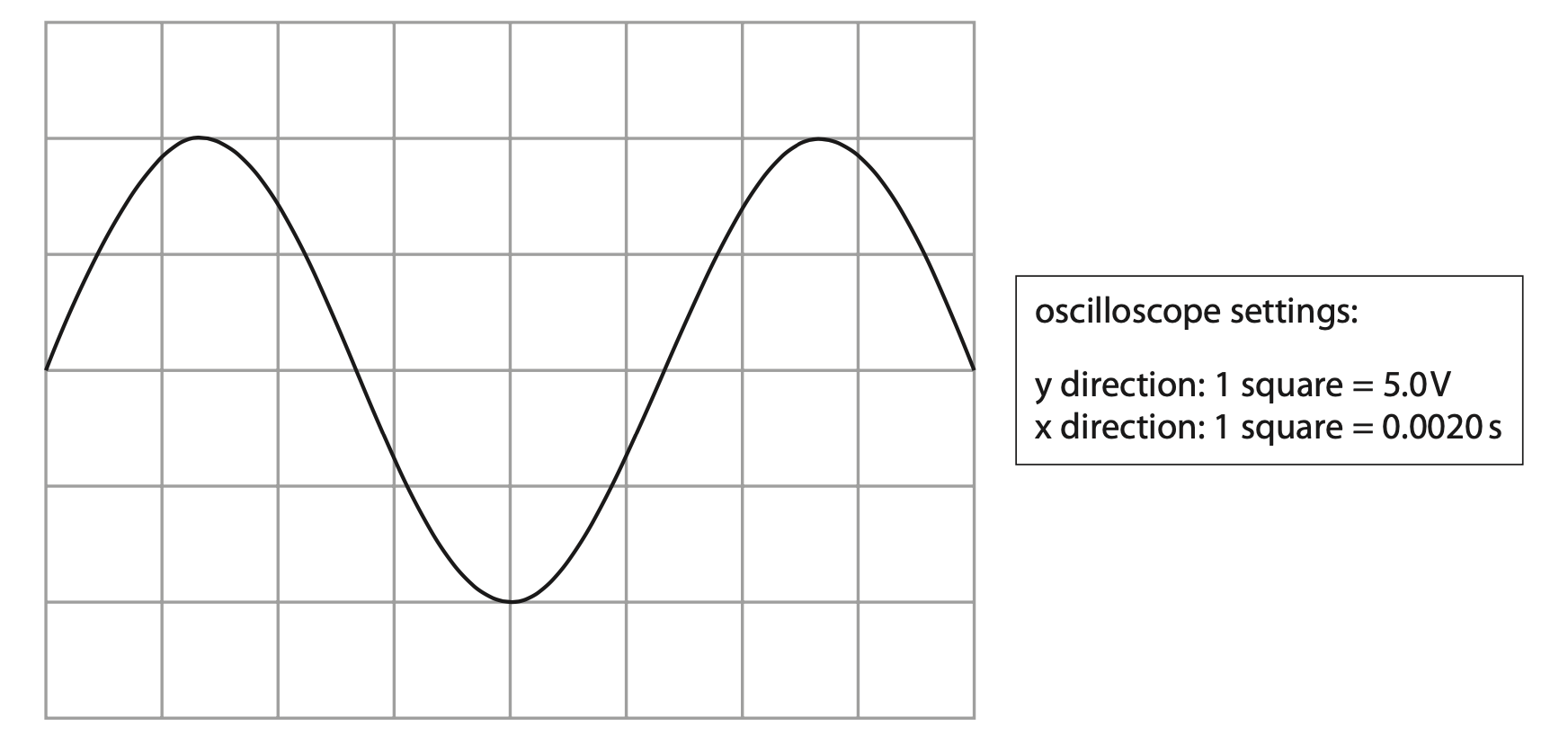
(a) Give the name of the piece of equipment that is connected to the oscilloscope to detect the sound wave. (1)
(b) (i) Use the trace on the oscilloscope to determine the time period of the detected sound wave. (2)
time period = …………………………………………………….. s
(ii) Calculate the frequency of the detected sound wave. (1)
frequency = …………………………………………………….. Hz
(c) (i) State the formula linking energy transferred, charge and voltage. (1)
(ii) The effective voltage of the oscilloscope trace can be calculated using the formula
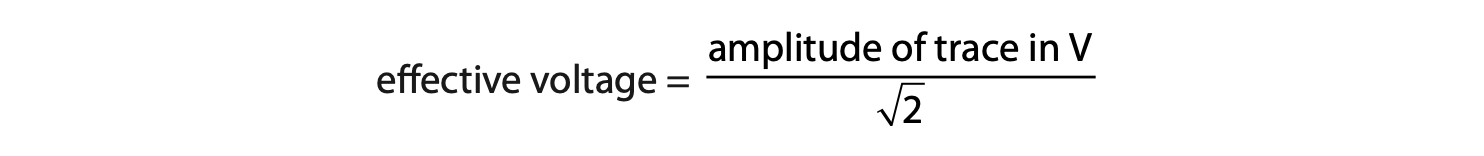
Use the effective voltage to calculate the energy transferred when 6.3 × 10−5 C of charge passes through the oscilloscope. (3)
energy transferred = …………………………………………………….. J
(Total for Question 7 = 8 marks)









