IGCSE Physics Magnetism & Electromagnetism Past Papers Exam Questions (Edexcel): 2021-22
We analysed the International GCSE past papers and grouped the questions by topic. Here, you will find questions relating to the topic – Magnetism and electromagnetism. Use these to familiarise, practice and prepare for your IGCSE Physics examination.
See IGCSE Physics Past Years Exam Questions from the topic Magnetism and electromagnetism 2019-20 for more questions.
What you need to know
Use the list below as a quick recap for what you need to know before attempting the past year exam questions under this topic. This is based on Edexcel International GCSE in Physics (4PH1) specification with first teaching Sept 2017 and first examination June 2019.
Paper 1 and 2: (6) Magnetism and electromagnetism
Paper 1 covers all the topics except where it is marked “Paper 2 only” while Paper 2 covers all topics.
A. Units
- ampere (A), volt (V) and watt (W)
B. Magnetism
- know that magnets repel and attract each other and attract magnetic substances
- be able to describe the properties of magnetically hard and soft materials
- understand the term magnetic field line
- know that a magnetic field can induce magnetism in some materials
- investigate magnetic field patterns
- how to use two bar magnets to produce a uniform magnetic field
C. Electromagnetism
- know that an electric current in a conductor produces a magnetic field around it
- describe the construction of electromagnets (Paper 2 only)
- draw magnetic field patterns for a straight wire, flat circular coil and solenoid when each is carrying a current (Paper 2 only)
- know that there is a force on a moving charged particle in a magnetic field (Paper 2 only)
- understand why a force is exerted on a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field, and how this effect is applied in dc motors and loudspeakers
- use the left hand rule to predict the direction of the resulting force when a wire carries a current perpendicular to a magnetic field
- describe how the force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field changes with the magnitude and direction of the field and current
D. Electromagnetic Induction
- know that a voltage is induced in a conductor or coil when it moves through a magnetic field or when a magnetic field changes through it and describe the factors that affect the size of the induced voltage
- describe the generation of electricity by the rotation of a coil within a magnetic field or rotating magnet in a coil
(Paper 2 only)
- describe the construction of a transformer, and understand that a transformer changes the size of an alternating voltage. (Paper 2 only)
- explain the use of step-up and step-down transformers in the large scale transmission of electrical energy. (Paper 2 only)
- relationship between input and output voltages and the turns ratio for a transformer. input (primary) voltage/ output (secondary) voltage = primary turns/secondary turns (Paper 2 only)
- relationship input power = output power Vp Ip =Vs Is for 100% efficiency (Paper 2 only)
January 2021 Paper 1P Q7
(Magnetism and Force and Motion)
7 Very strong magnets can be made using the element neodymium.
(a) Diagram 1 shows parts of two neodymium magnets, X and Y, when they are held close together
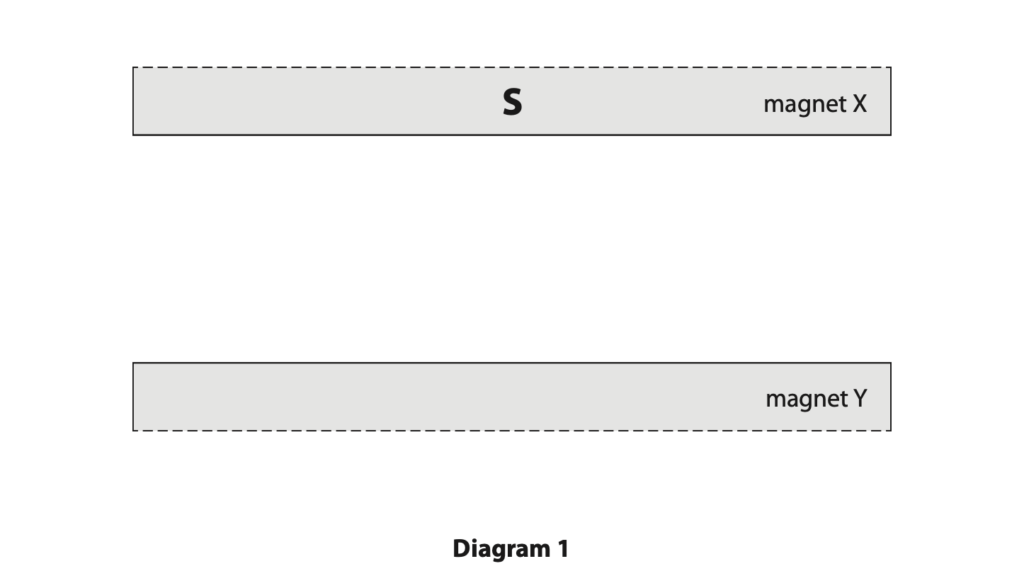
A uniform magnetic field is produced in the space between the magnets. Diagram 1 shows the south pole of magnet X.
Complete diagram 1 by drawing the uniform magnetic field and labelling the pole on magnet Y (3)
(b) Diagram 2 shows another neodymium magnet being used to lift an iron ball from a table.
The iron ball is shown at the instant it leaves the surface of the table.
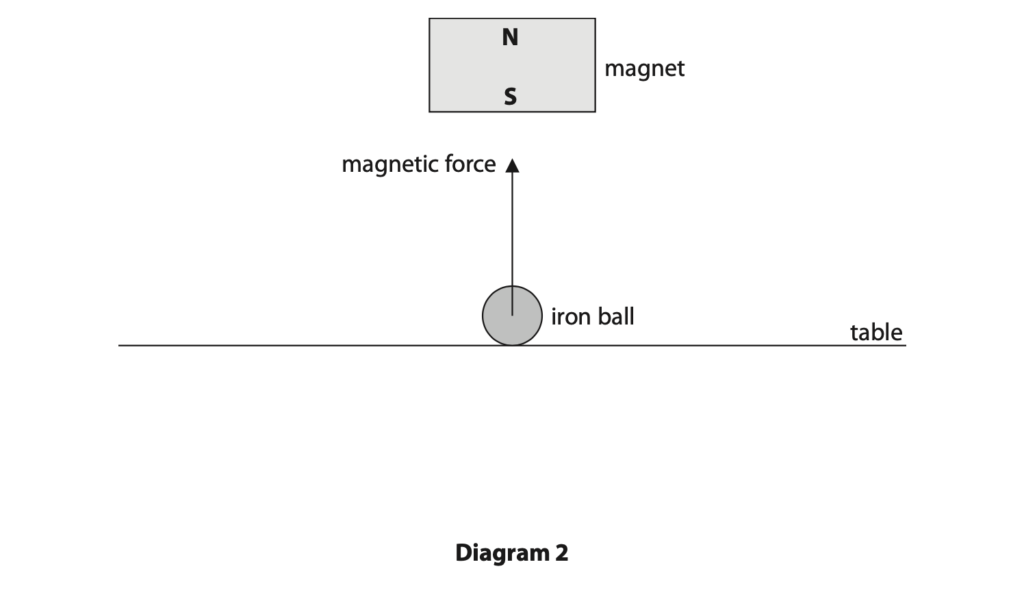
(i) Explain why the iron ball experiences an upward magnetic force. (2)
(ii) The iron ball experiences an upward resultant force at the instant shown in diagram 2.
Draw a labelled arrow on diagram 2 to show the weight of the iron ball. (1)
(iii) State the formula linking weight, mass and gravitational field strength. (1)
(iv) At the instant shown in diagram 2, the resultant force acting on the iron ball is 124 mN and the magnetic force is 165 mN.
Calculate the mass of the iron ball. (4)
mass of iron ball = …………………………………………………… kg
(v) Explain why the resultant force acting on the iron ball increases as the iron ball moves towards the magnet. (2)
(Total for Question 7 = 13 marks)
January 2021 Paper 2P Q5
5 Transformers are useful in the transmission of electricity.
(a) The diagram shows a step-down transformer.
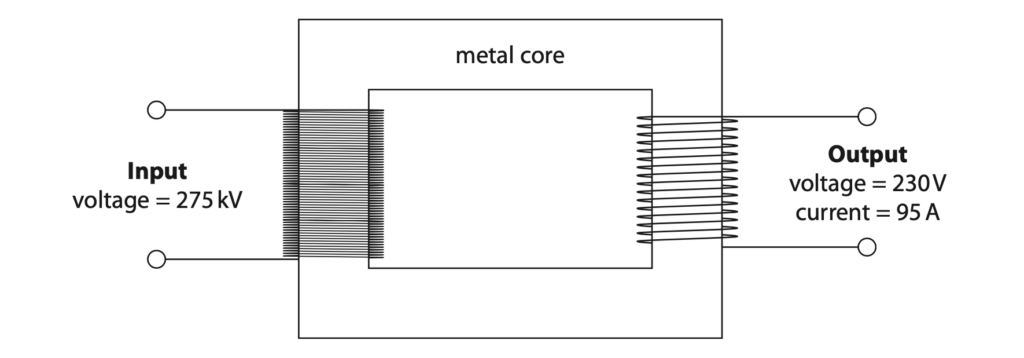
(i) Give the name of a suitable metal that could be used in the core of the transformer. (1)
(ii) State the formula linking input power and output power for a transformer. (1)
(iii) The step-down transformer has an input voltage of 275 kV and an output voltage of 230V.
The transformer has an output current of 95 A.
Calculate the input current to the transformer.
Assume the transformer is 100% efficient. (3)
input current = …………………………………………………….. A
(b) Explain how transformers are useful in the large-scale transmission of electricity.
You may draw a diagram to support your answer. (5)
(Total for Question 5 = 10 marks)
January 2021 Paper 1PR Q2
2 The diagram shows the apparatus used to demonstrate the existence of electromagnetic radiation just beyond the visible spectrum.
Electromagnetic radiation from the Sun passes through a slit and a prism. The electromagnetic radiation refracts through the prism onto the screen. Five thermometers are placed in front of the screen.
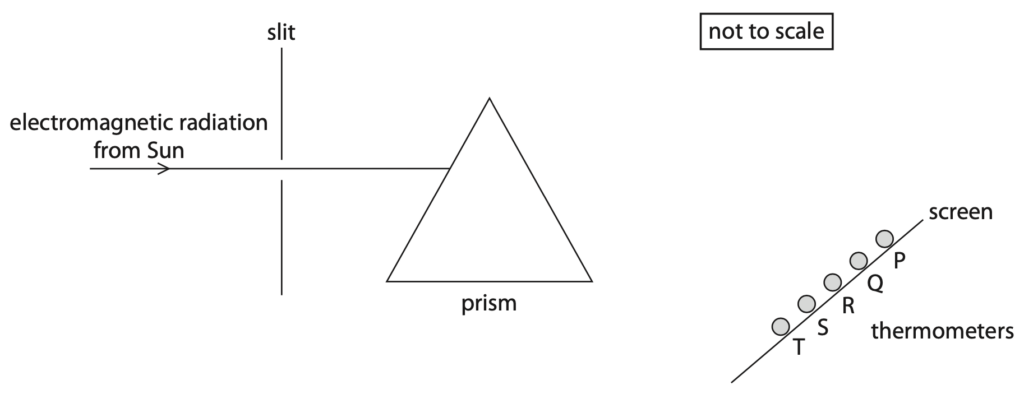
(a) Complete the table to show the missing parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. (3)
| Thermometer | Part of electromagnetic spectrum |
| P | |
| Q | red light |
| R | |
| S | violet light |
| T |
(b) Suggest why the lower part of each thermometer should be painted black. (2)
(c) The equipment is left for a short period of time.
The thermometers now show higher temperatures than before.
State the part of the electromagnetic spectrum in this demonstration that would give the largest temperature increase. (1)
(Total for Question 2 = 6 marks)
January 2021 Paper 1PR Q8
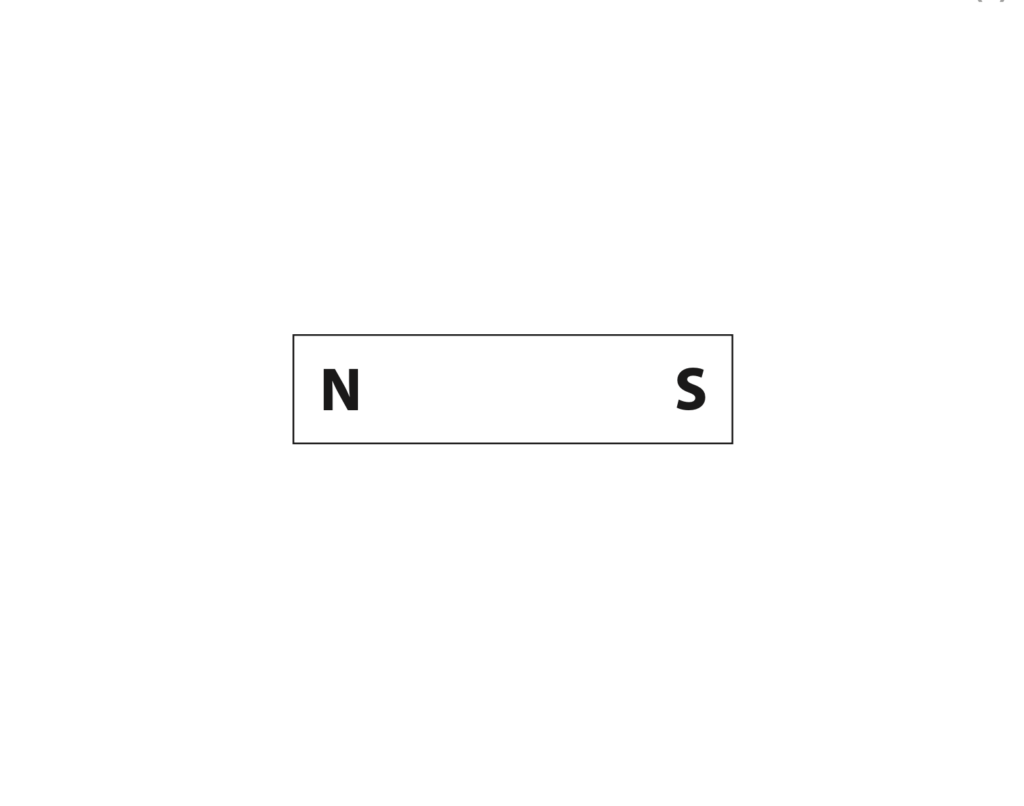
8 (a) The diagram shows a bar magnet.
Draw four magnetic field lines around the bar magnet.
(b) The diagram shows a loop of wire connected to the terminals of a voltmeter.
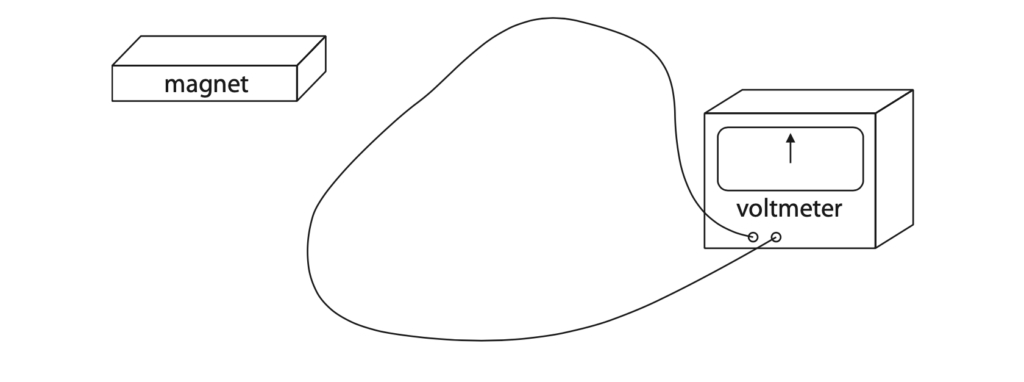
Explain why the voltmeter reading changes from zero when the magnet is moved near the loop of wire. (2)
(Total for Question 8 = 5 marks)
January 2021 Paper 2PR Q8
8 The diagram shows a step-down transformer.
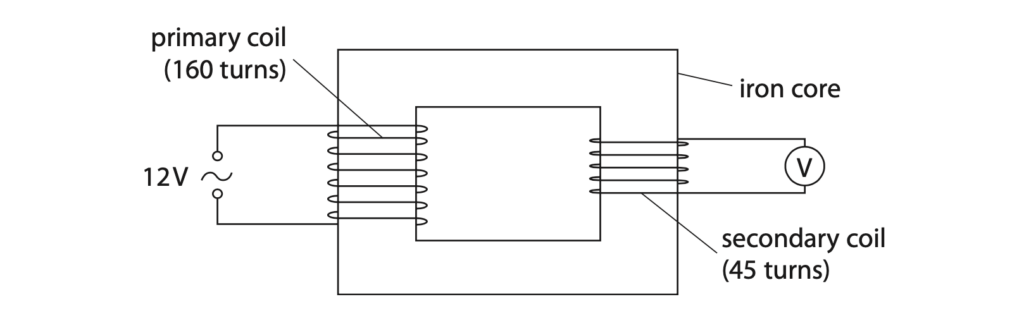
(a) Explain the operation of a step-down transformer. (4)
(b) (i) State the formula linking input voltage, output voltage and the turns ratio of a transformer. (1)
(ii) Calculate the output voltage for the transformer. (3)
(Total for Question 8 = 8 marks)
2020 Paper 1P Q1
1. The region of space around a magnet is known as a magnetic field.
(a) Which of these diagrams correctly represents the magnetic field around a bar magnet? (1)
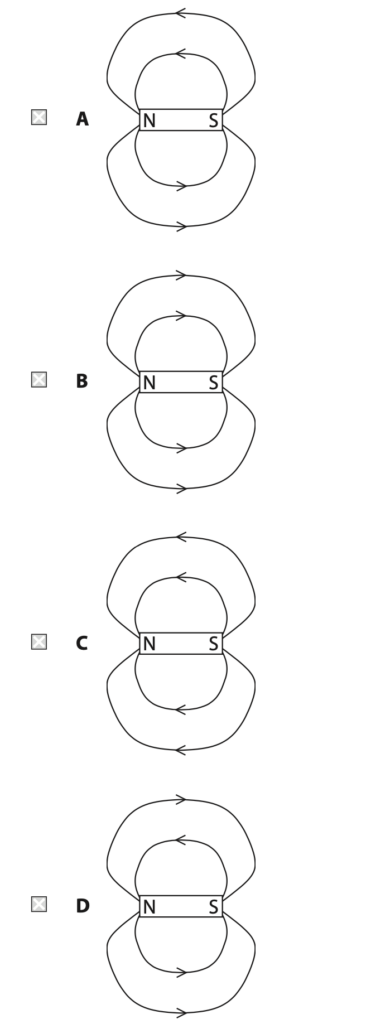
(b) The diagram shows two bar magnets placed close together.

(i) Which of these describes what happens to the two magnets? (1)
A nothing happens
B they attract
C they repel
D they spin
(ii) Which of these magnet arrangements gives a uniform field between the poles? (1)
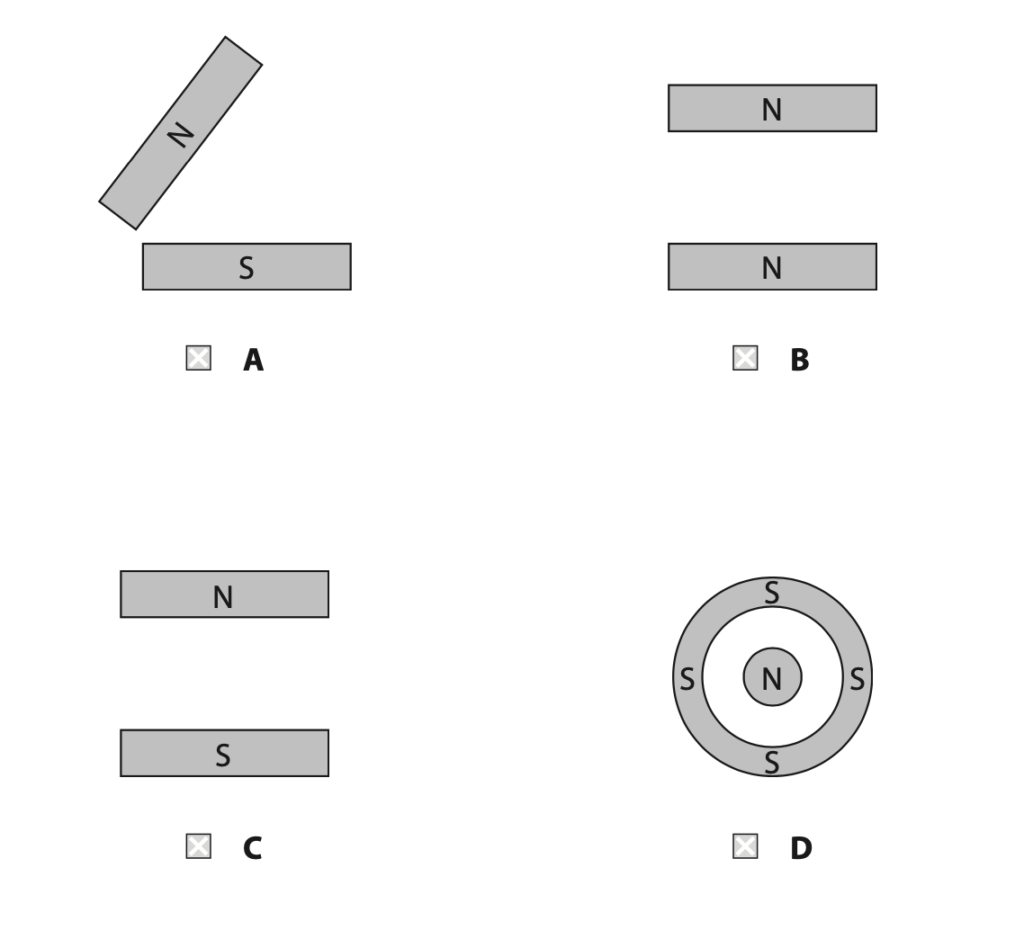
(c) State the name of a material that would be suitable for use as a permanent magnet. (1)
(d) Describe an investigation that could be used to determine the shape of the magnetic field around a bar magnet. (3)
(Total for Question 1 = 7 marks)
2022 Paper 1PR Q3
3 A student uses this apparatus to measure the force of repulsion between magnet A and magnet B.
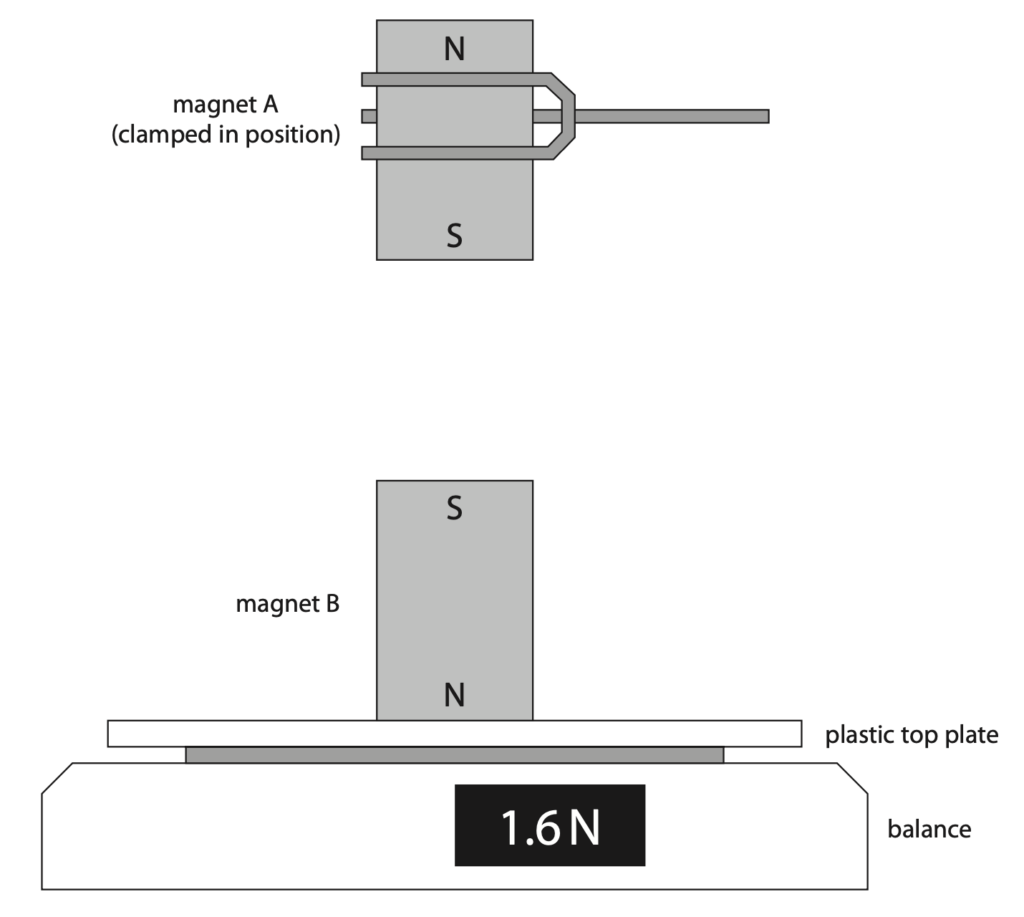
Magnet A is clamped in a fixed position.
Magnet B is resting on a balance.
(a) Give a reason why the two magnets shown in the diagram will repel each other. (1)
(b) Give a reason why the top plate of the balance is not affected by the magnetic fields of the magnets. (1)
(c) Complete the diagram by drawing the shape and direction of the magnetic field pattern between the magnets. (2)
(d) In the position shown, the balance reading is 1.6 N.
(i) Explain how the balance reading will change if magnet A is brought closer to magnet B. (2)
(ii) Explain how the balance reading will change if the poles of magnet A are reversed but the distance between the magnets remains constant. (2)
(Total for Question 3 = 8 marks)
2022 Paper 2P Q4
4 A student investigates how the strength of the magnetic field from a solenoid changes with distance from the end of the solenoid.
The diagram shows the solenoid connected to a power supply.
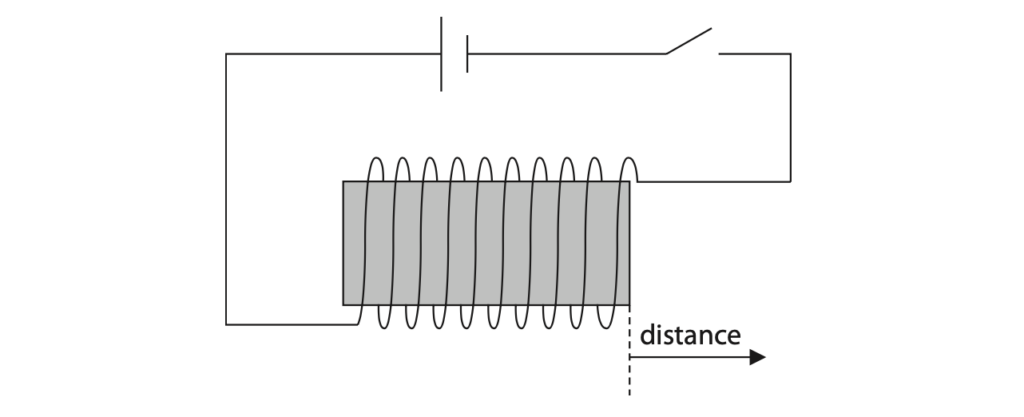
(a) The student uses a device called a Hall probe, which can be placed anywhere in the magnetic field to measure its strength at that point.
Design a suitable method for the investigation. Your answer should include
- any extra measuring equipment needed
- details of the independent variable, dependent variable and any control variables
You may include a diagram to help your answer. (5)
(b) The graph shows the results of the student’s investigation.
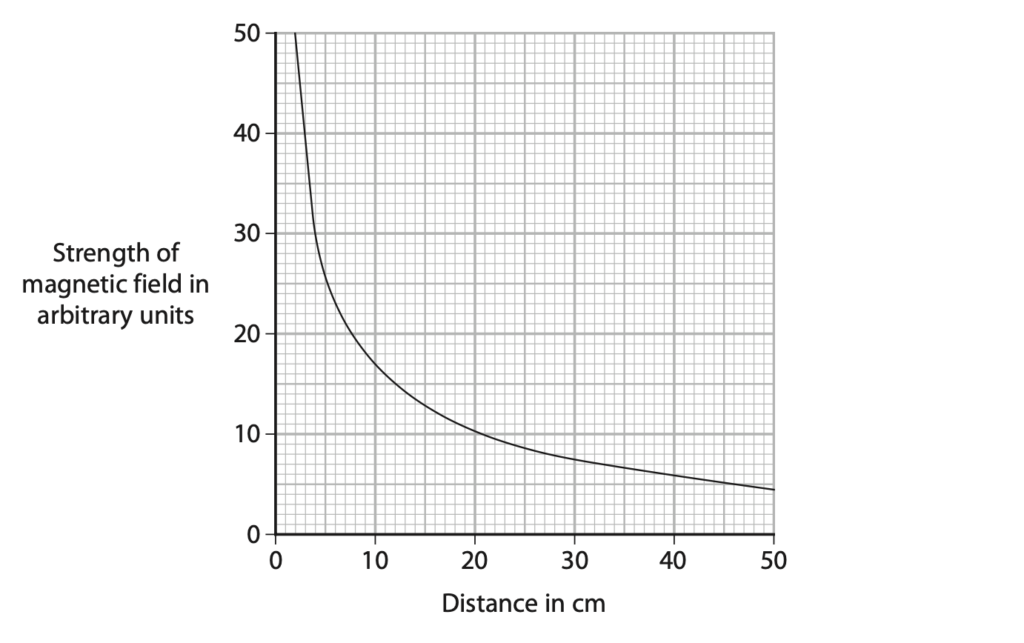
The student suggests that the relationship linking the strength of the magnetic field and the distance from the end of the solenoid is
strength of magnetic field × (distance)3 = constant
Use readings from the graph to deduce whether the results of the student’s investigation support this relationship. (4)
(Total for Question 4 = 9 marks)
2022 Paper 2P Q6
6 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machines can take scans of the inside of a patient.
(a) There is an electromagnet inside the MRI machine.
Describe the construction of an electromagnet.
You may draw a diagram to help your answer. (4)
(b) During the scan, music can be played through a loudspeaker to the patient.
The oscilloscope trace in the diagram represents a sound played to the patient.
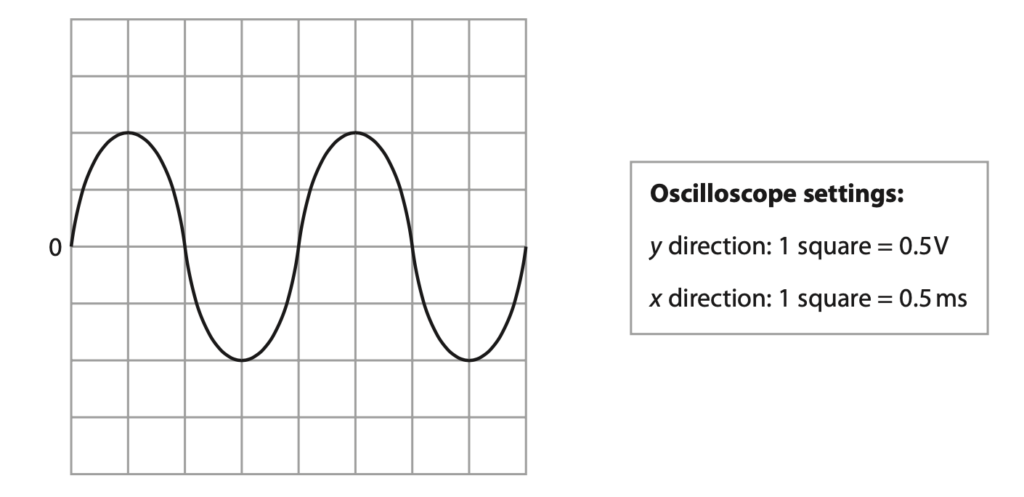
(i) Determine the period of the sound wave. (3)
period = …………………………………………………….. s
(ii) Calculate the frequency of the sound wave. (2)
frequency = …………………………………………………….. Hz
(iii) Deduce whether humans can hear the sound wave. (2)
(iv) The current in the loudspeaker is alternating current (a.c.).
Give the evidence from the oscilloscope trace to support this statement. (2)
(v) Draw the circuit symbol for an a.c. power supply. (1)
(Total for Question 6 = 14 marks)
2022 Paper 2PR Q8
8 Diagram 1 shows a machine used for demonstrating electrostatics.
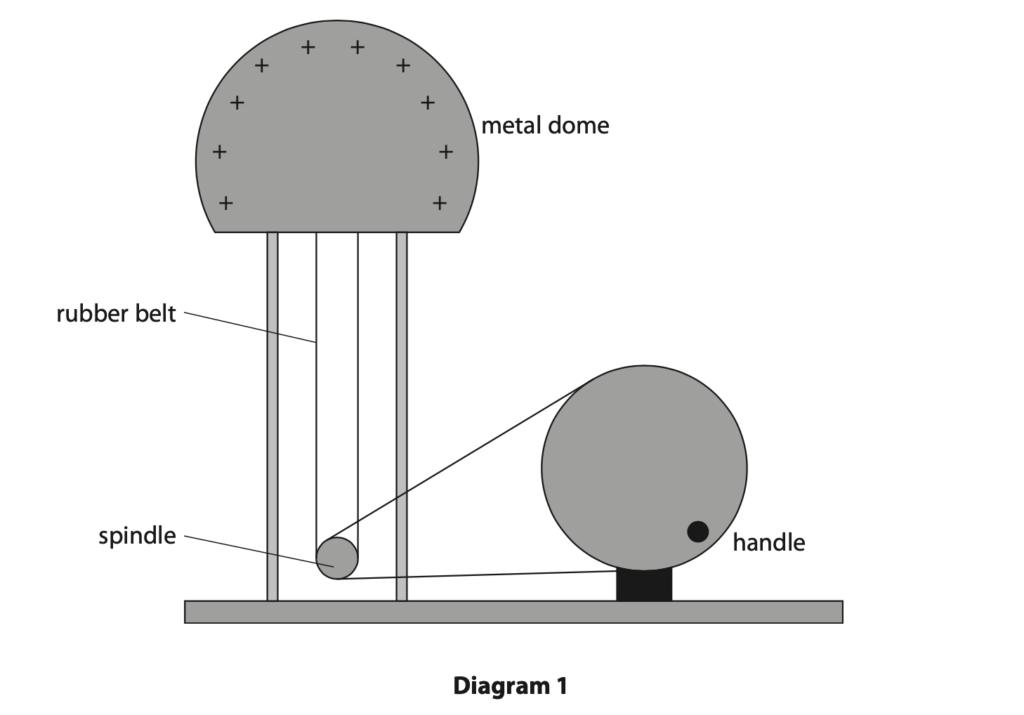
(a) When the handle is turned, the dome becomes positively charged.
(i) In terms of electron movement, give a reason why the metal dome becomes positively charged. (1)
(ii) When the handle is turned for 15 s the dome gains 0.50 J of energy in its electrostatic store as it becomes charged.
The voltage between the dome and the earth is 120 kV.
Calculate the mean charging current during this time. (3)
mean charging current = ……………………………………….. A
(b) The metal dome is discharged.
A thin metal case is then placed on top of the metal dome, as shown in Diagram 2.
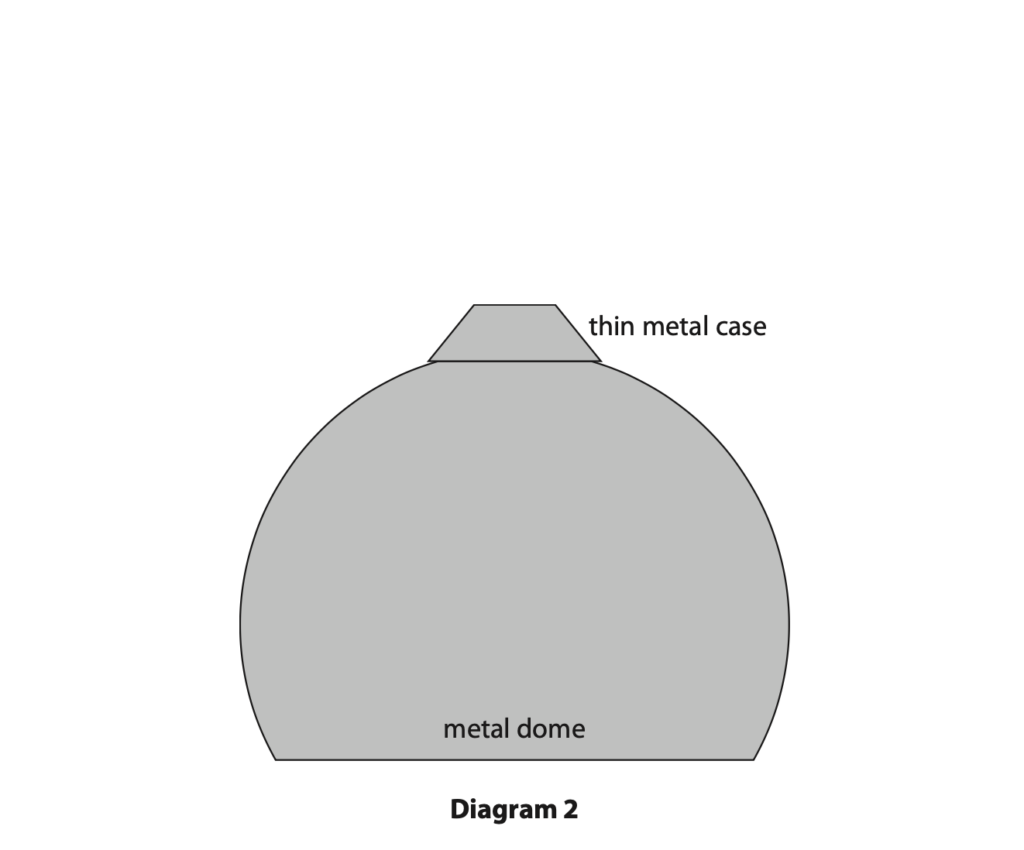
(i) When the handle is turned, the thin metal case moves upwards away from the dome.
Explain why the thin metal case starts to move upwards. (3)
(ii) Explain why the metal case reaches a maximum height above the metal dome. (4)
(Total for Question 8 = 11 marks)
















